100 Basis Points Equals 1 Percent
catholicpriest
Nov 26, 2025 · 10 min read
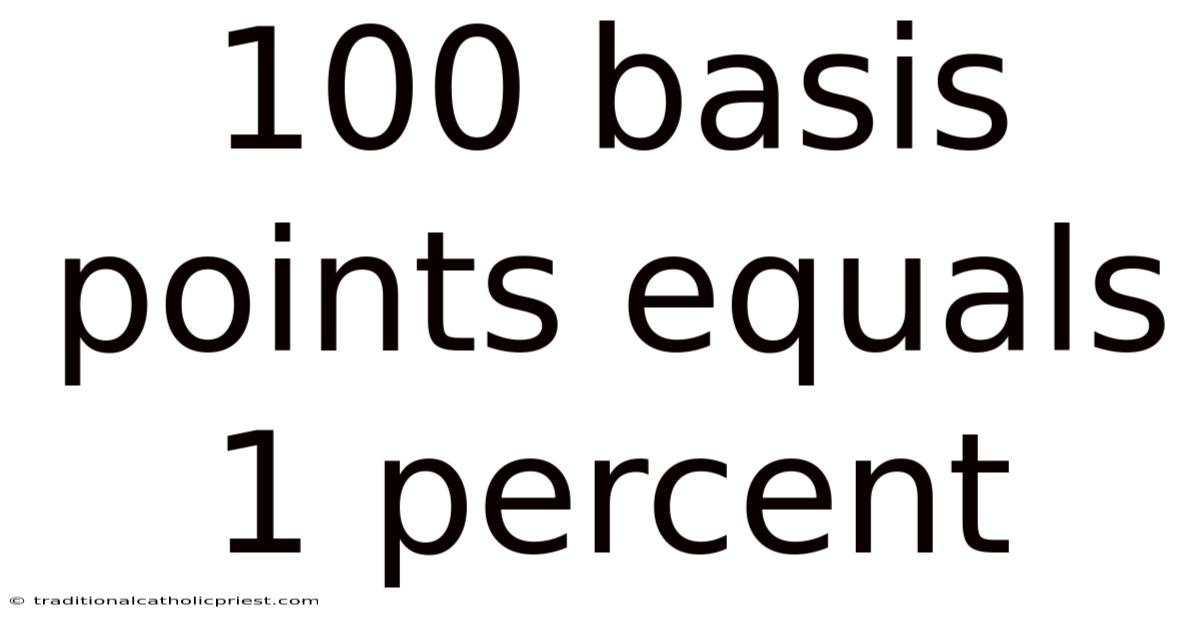
Table of Contents
Have you ever heard someone in the financial world say "basis points" and wondered what they were talking about? It might sound like complicated jargon, but it's actually a simple concept that's essential for understanding interest rates, yields, and other percentage-based changes in finance. Think of it as a way to speak precisely about very small changes, avoiding any ambiguity.
Imagine you're tracking the interest rate on your savings account. The bank announces an increase from 2.50% to 2.75%. That's a 0.25% increase, but it can also be described as a 25 basis point increase. This level of detail is crucial in finance, where even tiny fractions of a percentage can represent significant sums of money. This article will delve into the world of basis points, explaining why they're so important and how they're used in various financial contexts.
Main Subheading
In the financial world, precision is key. When dealing with large sums of money, even the smallest percentage change can have a significant impact. This is where the concept of basis points comes into play. A basis point is a unit of measure used in finance to describe the percentage change in the value or rate of a financial instrument. One basis point is equal to 0.01% or 1/100th of a percent. Therefore, 100 basis points equals 1 percent.
The primary reason for using basis points is to avoid ambiguity and to provide a more precise way of expressing changes in interest rates, yields, and other percentage-based figures. For instance, saying that an interest rate has increased by "one percent" could be confusing. Does it mean the rate went from 1% to 2% (a 100% increase), or from, say, 5% to 6% (a 20% increase)? By using basis points, such ambiguities are eliminated. A 100 basis point increase always means an increase of exactly 1%, regardless of the initial value.
Comprehensive Overview
To truly grasp the significance of basis points, it's essential to understand their definition, mathematical foundation, historical context, and how they are used across different financial instruments.
Definition and Mathematical Foundation
As mentioned earlier, one basis point is equivalent to 0.01% or 1/100th of a percent. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as:
1 basis point (bp) = 0.01% = 0.0001
To convert basis points to percentage, you simply divide the number of basis points by 100. Conversely, to convert a percentage to basis points, you multiply the percentage by 100. For example:
- 50 basis points = 50 / 100 = 0.50%
- 0.75% = 0.75 * 100 = 75 basis points
This simple mathematical relationship is fundamental to understanding how basis points are used in financial calculations and communications.
Historical Context
The use of basis points evolved over time as financial markets became more sophisticated and the need for precise communication increased. While the exact origin is difficult to pinpoint, the term gained prominence in the bond market. Bond yields are typically quoted in basis points, reflecting the need for accuracy in pricing and trading these instruments.
Before the widespread use of calculators and computers, dealing with small percentage changes manually could be cumbersome. Basis points provided a convenient way to express these changes without having to perform complex calculations each time. Over time, the use of basis points expanded to other areas of finance, including interest rates, mortgages, and derivatives.
Usage in Different Financial Instruments
1. Bonds: In the bond market, basis points are frequently used to describe changes in bond yields. For example, if a bond yield increases from 3.50% to 3.75%, it is said to have increased by 25 basis points. This level of precision is critical because even small changes in bond yields can have a significant impact on bond prices and overall investment returns.
2. Interest Rates: Central banks often use basis points when adjusting benchmark interest rates. For instance, if a central bank decides to lower its key interest rate by 0.25%, it would announce a 25 basis point cut. This affects borrowing costs across the economy, influencing everything from mortgage rates to business loans.
3. Mortgages: Mortgage rates are also often quoted and adjusted in basis points. A change of even a few basis points can affect the monthly payments and total interest paid over the life of a mortgage. For example, a 10 basis point increase on a $300,000 mortgage could result in thousands of dollars in additional interest over 30 years.
4. Loans: In the world of loans, whether they are personal, business, or otherwise, the interest rates are often defined and adjusted in terms of basis points. This allows both lenders and borrowers to understand and negotiate the terms with clarity.
5. Derivatives: Derivatives, such as interest rate swaps and options, also rely heavily on basis points. These instruments are used to manage risk and speculate on interest rate movements, so precise measurement is essential. Changes in interest rate expectations, even by a few basis points, can significantly impact the value of these complex financial products.
Significance in Financial Analysis
Basis points are not just a unit of measure; they also play a crucial role in financial analysis and decision-making. Here’s why:
1. Clarity: Basis points eliminate confusion by providing a standardized way to express percentage changes. This is especially important in complex financial transactions where multiple parties are involved.
2. Precision: Financial models and analyses often require a high degree of accuracy. Using basis points allows analysts to capture even the smallest changes, leading to more accurate forecasts and risk assessments.
3. Comparison: Basis points facilitate easy comparison of changes across different financial instruments and time periods. This helps investors and analysts identify trends, assess relative value, and make informed decisions.
4. Risk Management: In risk management, basis points are used to quantify and manage interest rate risk. Banks and other financial institutions use sophisticated models to measure the potential impact of interest rate changes on their portfolios, often expressed in terms of basis points.
Trends and Latest Developments
The use of basis points remains a standard practice in finance, but there are some interesting trends and developments to note:
1. Increased Volatility: In recent years, financial markets have experienced increased volatility, leading to more frequent and sometimes larger changes in interest rates and yields. This has made the precise measurement provided by basis points even more critical.
2. Quantitative Easing (QE): During periods of QE, central banks often use forward guidance to communicate their intentions regarding future interest rate policy. This guidance is typically expressed in terms of basis points, indicating the expected magnitude and timing of future rate changes.
3. Negative Interest Rates: In some countries, central banks have experimented with negative interest rates. In this context, basis points are used to describe how far below zero the rates have gone. For example, a rate of -0.50% would be expressed as -50 basis points.
4. Fintech and Algorithmic Trading: The rise of fintech and algorithmic trading has further emphasized the importance of precision in financial markets. These technologies rely on precise data and calculations to execute trades and manage risk, making basis points an essential unit of measure.
5. ESG Investing: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are increasingly influencing investment decisions. Analysts are using basis points to quantify the impact of ESG-related risks and opportunities on financial performance. For example, a company's cost of capital may be adjusted based on its ESG rating, with the adjustment expressed in basis points.
Tips and Expert Advice
Understanding and using basis points effectively can significantly enhance your financial literacy and decision-making. Here are some practical tips and expert advice:
1. Always Convert to Percentage: When you encounter basis points, take a moment to convert them to percentages. This will help you understand the magnitude of the change in a more intuitive way. For example, if you hear that a bond yield has increased by 75 basis points, quickly convert that to 0.75% to get a clear sense of the impact.
2. Pay Attention to Context: The significance of a basis point change depends on the context. A 10 basis point change in a short-term interest rate may have a different impact than a 10 basis point change in a long-term bond yield. Consider the overall market conditions and the specific financial instrument involved.
3. Use Basis Points in Your Own Calculations: When evaluating investment opportunities or making financial decisions, incorporate basis points into your own calculations. This will help you assess the potential risks and rewards with greater precision. For example, if you're comparing two investment options with slightly different yields, express the difference in basis points to quantify the advantage of one over the other.
4. Stay Informed: Keep up with financial news and analysis to understand how basis points are being used in the market. Pay attention to central bank announcements, economic reports, and market commentary. This will help you develop a deeper understanding of the factors that influence interest rates and yields.
5. Be Aware of Benchmarks: Understand the key benchmark interest rates that are used in your country or region. These benchmarks, such as the federal funds rate in the United States or the repo rate in other countries, serve as a reference point for other interest rates in the economy. Changes in these benchmarks, expressed in basis points, can have a ripple effect across financial markets.
6. Consider Professional Advice: If you're making complex financial decisions, consider seeking advice from a qualified financial advisor. A professional can help you understand the implications of basis point changes in the context of your overall financial goals and risk tolerance.
7. Understand the Impact on Investments: Small changes, when amplified by the size of an investment, can have a significant impact. Consider the compounding effect.
8. Factor in Inflation: Always consider inflation when evaluating interest rates and yields. The real interest rate, which is the nominal interest rate minus inflation, provides a more accurate picture of the true return on investment. Changes in inflation expectations can impact interest rates and yields, so it's important to factor this into your analysis.
FAQ
Q: Why are basis points used instead of percentages? A: Basis points provide a more precise and unambiguous way to express small percentage changes in finance.
Q: How do I convert basis points to percentage? A: Divide the number of basis points by 100 (e.g., 50 basis points = 0.50%).
Q: What is the origin of the term "basis point"? A: The term gained prominence in the bond market, reflecting the need for accuracy in pricing and trading bonds.
Q: Are basis points used only for interest rates? A: No, basis points are used to describe changes in yields, spreads, fees, and other percentage-based figures in finance.
Q: How do central banks use basis points? A: Central banks often use basis points when adjusting benchmark interest rates to influence borrowing costs and economic activity.
Q: What is the impact of a 1 basis point change on a mortgage? A: Even a small change like 1 basis point can affect the monthly payments and total interest paid over the life of a mortgage.
Conclusion
Understanding that 100 basis points equals 1 percent is fundamental to navigating the financial world. Basis points offer a precise, unambiguous way to describe small percentage changes, which is crucial in finance where even minor fluctuations can have significant impacts. Whether you're tracking interest rates, analyzing bond yields, or managing investments, being fluent in the language of basis points will enhance your financial literacy and decision-making.
Now that you're equipped with this knowledge, take the next step to deepen your understanding. Explore financial news, analyze market trends, and consider how basis points influence your own financial decisions. Share this article with friends and colleagues who could benefit from understanding this essential concept. And if you have further questions or insights, leave a comment below to join the conversation!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 100 Basis Points Equals 1 Percent . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.