What Is X Squared Plus X Squared
catholicpriest
Dec 04, 2025 · 11 min read
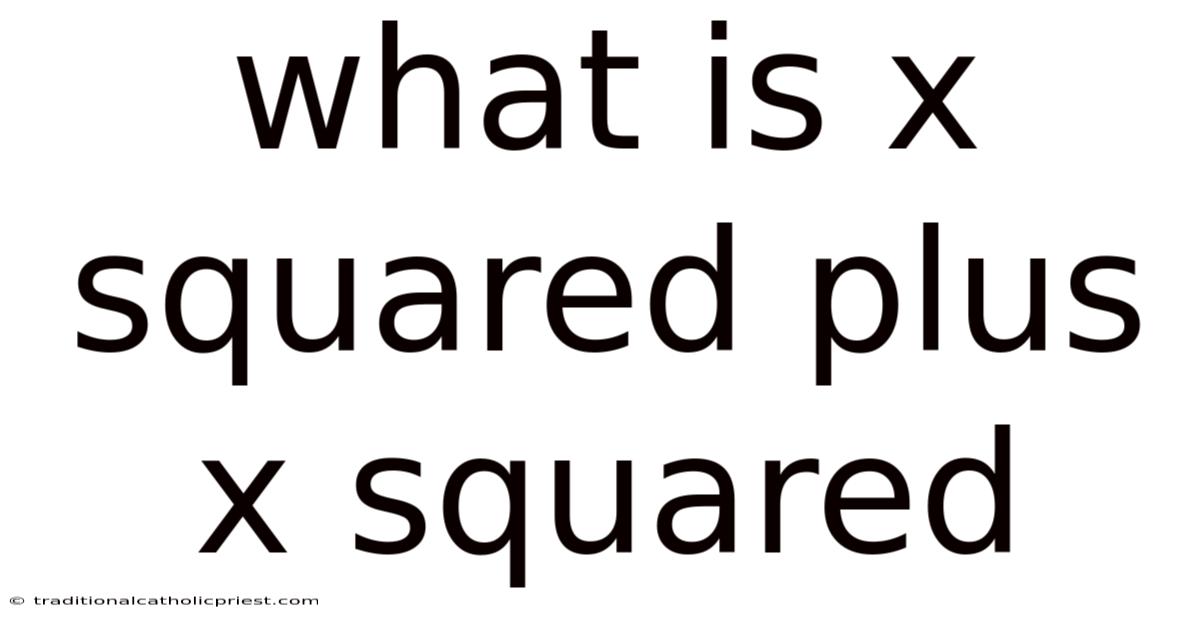
Table of Contents
Imagine you're arranging square tiles on a floor. You start with a group of tiles forming a perfect square, let's say 'x' tiles wide and 'x' tiles long – that's your 'x squared' or x². Now, someone comes along and says, "Great start! Now, give me another group of tiles exactly like that one." What do you have? You have your original square of tiles plus another identical square of tiles. How many tiles do you have in total? This simple scenario illustrates the core concept of what we're exploring: adding x² + x².
Perhaps you're baking cookies for a bake sale, and you decide to arrange them in a square pattern on a tray to make them look appealing. If you've arranged 'x' cookies in each row and 'x' cookies in each column, the total number of cookies on that tray is x². If you need to fill two trays, each with the same square arrangement, you're essentially dealing with x² + x². Understanding how to simplify this expression is fundamental not only in algebra but also in real-world applications like this one. This article dives into the mechanics, implications, and applications of x² + x², providing a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental algebraic concept.
Understanding the Basics of x² + x²
Before diving into the intricacies, let's solidify the groundwork. The expression x² + x² represents the addition of two identical terms, each being 'x' squared. The term 'x²' (read as "x squared") signifies 'x' multiplied by itself (x * x). This operation, known as squaring, is a fundamental concept in algebra and is used extensively in geometry to calculate areas and in physics to describe relationships between quantities.
At its heart, algebra is about simplifying expressions and solving equations. Expressions are combinations of variables (like 'x'), constants (like numbers), and operations (like +, -, *, /). Simplifying an expression means rewriting it in a more compact and understandable form without changing its value. In the case of x² + x², simplification is straightforward, following the basic rules of algebraic addition.
Definitions and Foundations
To fully grasp the concept, let's break down the key components:
- Variable: A symbol (usually a letter, like 'x') that represents an unknown or changing quantity.
- Constant: A fixed numerical value.
- Coefficient: A number that multiplies a variable. In the term 'x²', the coefficient is implicitly 1 (1 * x²).
- Exponent: A number that indicates how many times a base number is multiplied by itself. In 'x²', the exponent is 2, indicating that 'x' is multiplied by itself.
- Term: A single mathematical expression, which can be a variable, a constant, or a combination of both (e.g., x², 3x, 7).
The expression x² + x² consists of two like terms. Like terms are terms that have the same variable raised to the same power. Because both terms are 'x²', they can be combined. This combination is based on the distributive property, a core concept in algebra.
The Distributive Property and Combining Like Terms
The distributive property states that a(b + c) = ab + ac. In reverse, ab + ac = a(b + c). This principle allows us to factor out common factors from terms. While we don't explicitly factor in the simplest simplification of x² + x², understanding the distributive property is crucial for more complex algebraic manipulations.
When we add x² + x², we're essentially adding 1x² + 1x². We can factor out the x² to get x²(1 + 1). Since 1 + 1 = 2, the simplified expression becomes 2x². This demonstrates that adding two identical squared terms results in doubling the squared term.
Visualizing x² + x²
Visual representations often make abstract concepts more concrete. Imagine a square with sides of length 'x'. The area of this square is x². Now, picture another identical square. If you combine these two squares, you have a total area of 2x².
Alternatively, consider a graph. The function y = x² represents a parabola. The expression x² + x² = 2x² represents a different parabola, one that is vertically stretched by a factor of 2 compared to the original. For any given value of 'x', the y-value on the graph of y = 2x² will be twice the y-value on the graph of y = x².
Common Misconceptions
A common mistake is to confuse x² + x² with (x + x)². While both expressions involve 'x' and squaring, they are fundamentally different. As we established, x² + x² simplifies to 2x². On the other hand, (x + x)² simplifies to (2x)², which equals 4x². It's essential to remember the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS) and to apply the squaring operation to the entire term within the parentheses.
Another error is attempting to combine x² with terms that are not like terms, such as 'x' or a constant. Only terms with the same variable raised to the same power can be directly added or subtracted. For example, x² + x cannot be simplified further because x² and x are not like terms.
Historical Context
While the modern notation of using exponents to represent powers wasn't fully standardized until the 17th century, the concept of squaring a number has been around for millennia. The Babylonians, for example, used geometric methods to solve quadratic equations, implicitly understanding the concept of squaring. The Greeks, particularly Euclid, explored squares and their properties in their geometric constructions and theorems.
The development of algebraic notation, including the use of symbols for variables and exponents, allowed mathematicians to express and manipulate these concepts more efficiently. René Descartes, with his introduction of coordinate geometry, further solidified the connection between algebra and geometry, making visual representations of algebraic concepts, like x², more accessible.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the simplification of x² + x² itself is a well-established mathematical principle, its application and relevance continue to evolve with advancements in various fields. Modern trends leverage this basic concept in complex algorithms, data analysis, and computational models.
Data Science and Machine Learning
In data science, squaring is a fundamental operation used in calculating variances and standard deviations, which are measures of data dispersion. The sum of squared differences is a core component in many machine learning algorithms, including linear regression and least squares methods. These algorithms aim to minimize the sum of the squared differences between predicted and actual values. Therefore, understanding how to manipulate and simplify expressions involving squared terms is crucial for optimizing these models.
Furthermore, in areas like image processing and computer vision, operations involving squares are used for tasks such as edge detection and image smoothing. The magnitude of gradients, often calculated using squared differences, helps identify sharp changes in pixel intensity, indicating edges.
Computational Mathematics
In computational mathematics, dealing with large-scale computations involving polynomials and series is common. Simplifying expressions containing squared terms can significantly reduce computational complexity and improve the efficiency of algorithms. For instance, in finite element analysis, which is used to solve complex engineering problems, the accurate and efficient calculation of squared terms is essential for obtaining reliable results.
Quantum Computing
Even in emerging fields like quantum computing, the concept of squaring finds application. Quantum states are often represented using complex numbers, and the probability of measuring a particular state is proportional to the square of the magnitude of the complex amplitude. Understanding how to manipulate and simplify expressions involving squared magnitudes is essential for analyzing and interpreting quantum computations.
Educational Approaches
Educational approaches are also evolving to make these concepts more accessible. Interactive simulations and visual tools are increasingly used to demonstrate the properties of squares and how they relate to algebraic expressions. These tools can help students develop a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts and avoid common misconceptions.
Expert Insights
Experts in mathematics education emphasize the importance of connecting abstract algebraic concepts to concrete examples and real-world applications. By showing students how squaring and the simplification of expressions like x² + x² relate to practical problems, educators can increase student engagement and motivation.
Furthermore, the use of technology, such as computer algebra systems (CAS), can help students explore and visualize algebraic concepts. These tools allow students to manipulate expressions, solve equations, and graph functions, providing a dynamic and interactive learning experience. However, experts caution against relying solely on technology and emphasize the importance of developing a strong foundation in the fundamental principles of algebra.
Tips and Expert Advice
Mastering the simplification of expressions like x² + x² involves more than just memorizing the rule. Here are some practical tips and expert advice to deepen your understanding and improve your problem-solving skills:
Practice Regularly
The key to mastering any mathematical concept is consistent practice. Work through a variety of problems involving the simplification of algebraic expressions, starting with simple examples and gradually progressing to more complex ones. This will help you develop fluency and confidence in your abilities. Don't just passively read through solutions; actively try to solve the problems yourself.
One effective strategy is to create your own practice problems. Vary the coefficients and exponents to challenge yourself and reinforce your understanding. For example, try simplifying expressions like 3x² + 5x² or 7x² - 2x².
Visualize the Concepts
As mentioned earlier, visual representations can be incredibly helpful for understanding abstract concepts. Whenever you encounter an algebraic expression, try to visualize what it represents. In the case of x² + x², picture two identical squares being combined. This can help you develop a more intuitive understanding of the concept.
Use online graphing tools to visualize functions involving squared terms. This can help you see how changing the coefficients affects the shape of the graph and the relationship between the variables.
Understand the Underlying Principles
Don't just memorize rules and formulas; strive to understand the underlying principles behind them. In the case of simplifying x² + x², understanding the distributive property and the concept of like terms is crucial. This will allow you to apply these principles to a wider range of problems and avoid common mistakes.
Take the time to review the definitions of key terms and concepts. Make sure you understand what a variable, a constant, a coefficient, and an exponent are. This will provide a solid foundation for your algebraic understanding.
Break Down Complex Problems
When faced with a complex algebraic expression, break it down into smaller, more manageable parts. Identify the like terms and combine them separately. This will make the problem less daunting and easier to solve.
Use parentheses to group terms and clarify the order of operations. This can help you avoid mistakes and ensure that you are applying the correct operations in the correct order.
Seek Help When Needed
Don't be afraid to ask for help when you are struggling with a concept. Talk to your teacher, a tutor, or a classmate. Explaining your difficulties to someone else can often help you clarify your own understanding.
Utilize online resources, such as educational websites and forums, to find explanations, examples, and practice problems. There are many excellent resources available that can help you improve your algebraic skills.
Apply to Real-World Scenarios
Look for opportunities to apply algebraic concepts to real-world scenarios. This will help you see the relevance of what you are learning and make it more engaging. For example, you can use algebra to calculate areas, volumes, and distances.
Think about how squared terms are used in fields like engineering, physics, and finance. This can help you appreciate the importance of algebra in these disciplines and motivate you to learn more.
FAQ
Q: What is the simplified form of x² + x²? A: The simplified form of x² + x² is 2x².
Q: Why can x² + x² be simplified, but x² + x cannot? A: x² + x² can be simplified because they are like terms (same variable raised to the same power). x² and x are not like terms, so they cannot be combined directly.
Q: Is 2x² the same as (2x)²? A: No, 2x² means 2 multiplied by x squared, while (2x)² means 2x multiplied by itself, which equals 4x².
Q: How does the distributive property apply to simplifying x² + x²? A: While not explicitly factored, understanding the distributive property is key. We can think of x² + x² as 1x² + 1x², then factor out x² to get x²(1 + 1), which simplifies to 2x².
Q: Where is x² + x² used in real-world applications? A: While the simplified form 2x² might not be directly visible, squaring is a fundamental operation in various fields like data science (variance calculations), geometry (area calculations), and physics (energy calculations). Understanding the underlying concept is what matters.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of algebra, such as simplifying the expression x² + x² to 2x², is more than just an academic exercise; it's a foundational skill with applications across numerous fields. By grasping the concepts of like terms, the distributive property, and the importance of visualization, you can build a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical studies.
Continue to practice, explore, and connect these concepts to real-world scenarios. To further enhance your understanding, consider exploring related topics such as polynomial arithmetic, quadratic equations, and the applications of algebra in various scientific and engineering disciplines. Share this article with others who might benefit, and leave a comment below with your questions or insights. What other algebraic concepts would you like to explore?
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Square A Trinomial
Dec 04, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 5 5 En Centimetros
Dec 04, 2025
-
2 3 Is Equivalent To What Fraction
Dec 04, 2025
-
What Does When It Rains It Pours Mean
Dec 04, 2025
-
How Many Thousands In A Trillion
Dec 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is X Squared Plus X Squared . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.