What Is 4 5 1 6 As A Fraction
catholicpriest
Dec 02, 2025 · 12 min read
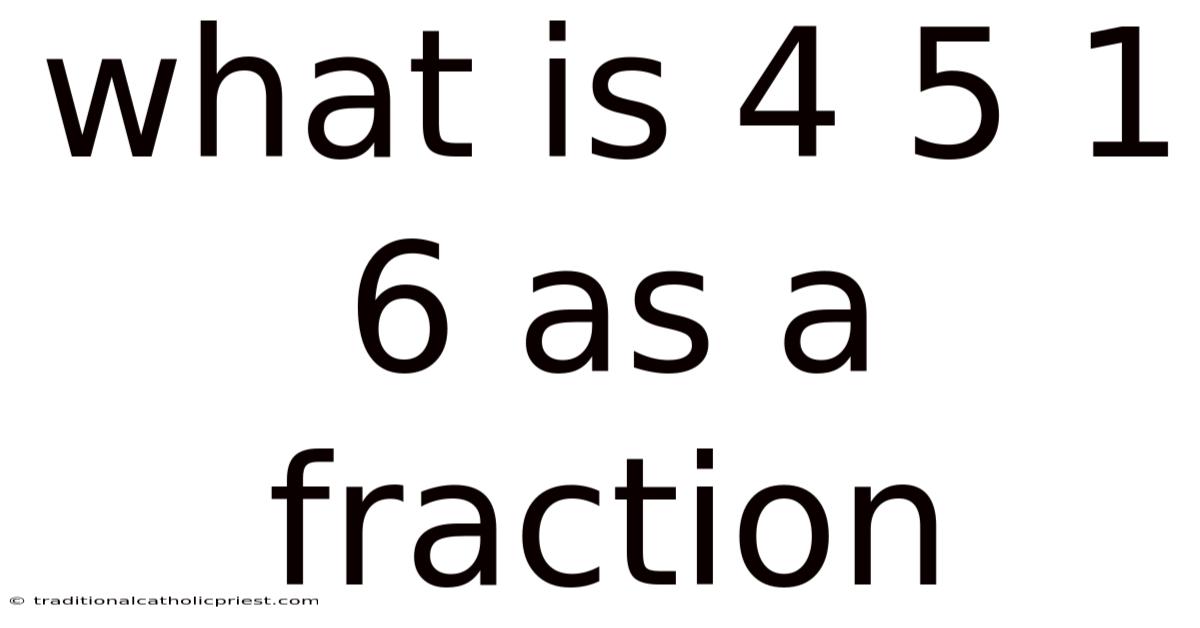
Table of Contents
The question "what is 4.516 as a fraction?" often arises when we need to perform precise calculations, convert measurements, or simply understand the relationship between decimal and fractional representations. Converting decimals to fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics, applicable in various fields from everyday tasks to complex scientific computations. In this article, we'll break down the process of converting the decimal 4.516 into a fraction, discuss the underlying principles, explore real-world applications, and provide expert tips to master this skill.
Converting Decimals to Fractions: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting a decimal like 4.516 into a fraction involves understanding the place value of each digit after the decimal point. In the decimal 4.516, the 5 is in the tenths place, the 1 is in the hundredths place, and the 6 is in the thousandths place. This understanding forms the basis for converting the decimal into a fraction. The process is straightforward but requires careful attention to detail to ensure accuracy. The ultimate goal is to express the decimal as a ratio of two integers, a numerator and a denominator, in its simplest form.
Decimals and fractions are two different ways of representing numbers that are not whole numbers. A decimal uses a base-10 system, where each digit after the decimal point represents a fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10 (e.g., 10, 100, 1000, etc.). Fractions, on the other hand, represent a part of a whole and are written as a ratio of two numbers, the numerator and the denominator. The denominator indicates the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into, and the numerator indicates how many of those parts are being considered. Converting between decimals and fractions allows us to express quantities in the most convenient and appropriate form for a given situation.
Comprehensive Overview
Definitions and Basics
A decimal is a number expressed in the base-10 system, using a decimal point to separate the whole number part from the fractional part. Each digit after the decimal point represents a power of 10. For example, in the decimal 4.516:
- The 4 is in the ones place.
- The 5 is in the tenths place (5/10).
- The 1 is in the hundredths place (1/100).
- The 6 is in the thousandths place (6/1000).
A fraction is a way to represent a part of a whole. It consists of two parts: the numerator (the top number) and the denominator (the bottom number). The numerator represents the number of parts we have, and the denominator represents the total number of parts. For example, in the fraction 1/2, 1 is the numerator, and 2 is the denominator.
Converting decimals to fractions involves expressing the decimal as a fraction with a power of 10 as the denominator and then simplifying the fraction to its lowest terms.
Scientific Foundations
The conversion of decimals to fractions is based on the fundamental principles of place value in the base-10 number system. Each position to the right of the decimal point represents a negative power of 10. For instance:
- Tenths place: (10^{-1} = \frac{1}{10})
- Hundredths place: (10^{-2} = \frac{1}{100})
- Thousandths place: (10^{-3} = \frac{1}{1000})
When converting a decimal to a fraction, we are essentially rewriting the decimal as a sum of fractions with denominators that are powers of 10. For example, 4.516 can be expressed as:
[ 4 + \frac{5}{10} + \frac{1}{100} + \frac{6}{1000} ]
This sum can then be combined into a single fraction with a common denominator.
Step-by-Step Conversion of 4.516 to a Fraction
To convert the decimal 4.516 into a fraction, follow these steps:
-
Write the decimal as a fraction with a power of 10 as the denominator:
Since 4.516 has three digits after the decimal point, we use 1000 (10^3) as the denominator:
[ 4.516 = \frac{4516}{1000} ]
-
Simplify the fraction:
To simplify the fraction, find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and the denominator. The GCD is the largest number that divides both the numerator and the denominator without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD of 4516 and 1000 is 4.
Divide both the numerator and the denominator by the GCD:
[ \frac{4516 \div 4}{1000 \div 4} = \frac{1129}{250} ]
So, the simplified fraction is (\frac{1129}{250}).
-
Express as a Mixed Number (Optional):
If desired, you can express the improper fraction (\frac{1129}{250}) as a mixed number. Divide 1129 by 250:
[ 1129 \div 250 = 4 \text{ remainder } 129 ]
Thus, the mixed number is (4 \frac{129}{250}).
Therefore, 4.516 as a fraction is (\frac{1129}{250}), or as a mixed number, (4 \frac{129}{250}).
History and Evolution
The concept of decimals and fractions has evolved over centuries. Ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and Babylonians, used fractions in their calculations, although their notation differed significantly from modern notation. The decimal system, as we know it today, was developed much later.
- Ancient Egypt: Egyptians used unit fractions (fractions with a numerator of 1) to perform calculations. Their system was cumbersome but effective for practical purposes like land measurement and construction.
- Babylon: Babylonians used a base-60 number system, which is still reflected in our measurement of time (60 seconds in a minute, 60 minutes in an hour) and angles (360 degrees in a circle). They had a sophisticated understanding of fractions.
- Medieval Islamic World: Islamic mathematicians made significant contributions to the development of algebra and number theory, including the refinement of fractional notation.
- Renaissance Europe: The widespread use of decimal fractions in Europe began in the late 16th century, largely due to the work of Simon Stevin, a Flemish mathematician. His book "De Thiende" (The Tenth) explained how to perform arithmetic operations using decimal fractions, making them more accessible and practical for everyday calculations.
Significance in Mathematics and Beyond
The ability to convert between decimals and fractions is crucial in various areas of mathematics, including algebra, calculus, and number theory. It also has practical applications in fields such as:
- Engineering: Engineers often need to perform precise calculations involving measurements and tolerances. Converting between decimals and fractions allows them to work with the most appropriate representation for a given task.
- Finance: Financial calculations, such as interest rates and currency conversions, often involve decimals and fractions. Understanding how to convert between them is essential for accurate financial analysis.
- Science: Scientists use decimals and fractions in experiments, data analysis, and modeling. For example, when measuring concentrations or calculating ratios, converting between decimals and fractions can simplify calculations.
- Everyday Life: In daily activities, such as cooking, measuring ingredients, or calculating proportions, converting between decimals and fractions helps ensure accuracy and consistency.
Trends and Latest Developments
Current Trends
The use of decimals and fractions remains fundamental in both academic and professional settings. Several trends influence how these concepts are taught and applied:
- Emphasis on Conceptual Understanding: Modern mathematics education emphasizes a deeper understanding of why decimals and fractions work the way they do, rather than rote memorization of procedures. This approach helps students develop better problem-solving skills and a more intuitive grasp of mathematical concepts.
- Integration of Technology: Calculators, software, and online tools have made it easier to convert between decimals and fractions. These tools reduce the risk of errors and allow users to focus on the broader context of their calculations.
- Real-World Applications: Educators are increasingly using real-world examples to illustrate the relevance of decimals and fractions. This helps students see how these concepts apply to their lives and motivates them to learn.
Data and Popular Opinions
According to educational research, students who have a strong understanding of decimals and fractions perform better in higher-level mathematics courses. A study by the National Mathematics Advisory Panel found that proficiency with fractions is a strong predictor of success in algebra and subsequent math courses.
Popular opinion among educators and mathematicians is that a solid foundation in decimals and fractions is essential for mathematical literacy. Many believe that these concepts should be taught early and reinforced throughout the curriculum to ensure that students develop a deep and lasting understanding.
Professional Insights
From a professional standpoint, proficiency in converting decimals to fractions is a valuable skill in many industries. Engineers, scientists, and financial analysts often need to work with both decimals and fractions and must be able to convert between them quickly and accurately.
In the field of data science, understanding decimals and fractions is essential for data normalization and scaling. Many machine learning algorithms require data to be scaled to a specific range, such as 0 to 1, which often involves converting decimals to fractions or vice versa.
Tips and Expert Advice
Practical Tips for Decimal to Fraction Conversion
-
Understand Place Value: Always start by identifying the place value of the last digit in the decimal. This will determine the denominator of the fraction. Example: In 4.516, the 6 is in the thousandths place, so the denominator will be 1000.
-
Write the Decimal as a Fraction: Write the decimal as a fraction with the decimal number as the numerator and the corresponding power of 10 as the denominator. Example: (4.516 = \frac{4516}{1000})
-
Simplify the Fraction: Find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator and divide both by the GCD to simplify the fraction. Example: The GCD of 4516 and 1000 is 4. ( \frac{4516 \div 4}{1000 \div 4} = \frac{1129}{250})
-
Use Prime Factorization: If you have trouble finding the GCD, use prime factorization. Break down both the numerator and the denominator into their prime factors and cancel out common factors. Explanation: Prime factorization can make it easier to identify common factors, especially for larger numbers.
-
Convert to Mixed Number (if applicable): If the numerator is greater than the denominator, convert the improper fraction to a mixed number. Example: (\frac{1129}{250} = 4 \frac{129}{250})
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
-
Incorrectly Identifying Place Value: A common mistake is misidentifying the place value of the digits after the decimal. Always double-check the place value to ensure you use the correct power of 10 as the denominator. Solution: Practice identifying place values with different decimals to build confidence.
-
Forgetting to Simplify: Failing to simplify the fraction is another common mistake. Always simplify the fraction to its lowest terms to get the most accurate and concise representation. Solution: After converting to a fraction, always look for common factors between the numerator and denominator.
-
Arithmetic Errors: Making mistakes in arithmetic, such as division or finding the GCD, can lead to incorrect conversions. Solution: Use a calculator to double-check your calculations, or practice arithmetic skills regularly.
Advanced Techniques
-
Using Continued Fractions: Continued fractions provide an alternative way to represent real numbers, including decimals. While not always practical for simple conversions, they can be useful for approximating irrational numbers. Explanation: Continued fractions can offer insights into the structure of real numbers and their approximations.
-
Floating-Point Representation: In computer science, floating-point numbers are used to represent real numbers in a computer's memory. Understanding how floating-point numbers are stored can help you understand the limitations of decimal representation in computers. Explanation: Floating-point representation involves storing a number as a base, an exponent, and a mantissa, which can lead to rounding errors in certain cases.
Real-World Examples
-
Cooking and Baking: When adjusting recipes, you often need to convert between decimal and fractional measurements. Example: A recipe calls for 0.75 cups of flour. Converting this to a fraction gives you (\frac{3}{4}) cups, which is easier to measure with standard measuring cups.
-
Construction and Carpentry: When working on construction projects, precise measurements are crucial. Converting decimals to fractions allows you to work with standard units and ensure accuracy. Example: A blueprint specifies a length of 2.625 inches. Converting this to a fraction gives you (2 \frac{5}{8}) inches, which can be easily measured with a ruler or tape measure.
-
Financial Analysis: In finance, interest rates and returns are often expressed as decimals. Converting these to fractions can help you understand the underlying ratios and proportions. Example: An interest rate of 0.05 can be converted to the fraction (\frac{1}{20}), representing a 5% return.
FAQ
Q: How do I convert a repeating decimal to a fraction? A: Converting repeating decimals to fractions involves setting up an algebraic equation and solving for the fraction. For example, if x = 0.333..., then 10x = 3.333.... Subtracting the first equation from the second gives 9x = 3, so x = 3/9, which simplifies to 1/3.
Q: What is the difference between a rational and an irrational number? A: A rational number can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. An irrational number cannot be expressed in this form. Examples of rational numbers include 0.5 (1/2) and 0.333... (1/3), while examples of irrational numbers include π and √2.
Q: Can all decimals be converted to fractions? A: Yes, all terminating and repeating decimals can be converted to fractions. However, non-repeating, non-terminating decimals (irrational numbers) cannot be expressed as exact fractions, but they can be approximated to a certain degree of accuracy.
Q: Why is it important to simplify fractions after converting them from decimals? A: Simplifying fractions makes them easier to understand and work with. Simplified fractions are in their lowest terms, meaning the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1. This provides the most concise and accurate representation of the quantity.
Q: Are there any online tools that can help with decimal to fraction conversion? A: Yes, there are many online tools and calculators that can convert decimals to fractions. These tools can be helpful for checking your work or for quickly converting decimals in practical applications. Examples include websites like CalculatorSoup and Mathway.
Conclusion
Converting the decimal 4.516 to a fraction results in (\frac{1129}{250}) or (4 \frac{129}{250}) as a mixed number. Mastering the conversion of decimals to fractions is a fundamental skill with wide-ranging applications in mathematics, science, engineering, and everyday life. By understanding the underlying principles, following a step-by-step approach, and practicing regularly, you can confidently convert any decimal to a fraction. Understanding decimal to fraction conversions empowers you to tackle real-world problems with precision and clarity.
We encourage you to practice these conversions and explore additional resources to deepen your understanding. Try converting other decimals to fractions and see how these skills can be applied in your daily life. Share your experiences and questions in the comments below to continue the learning journey.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 4 5 1 6 As A Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.