Symbol For Is Not Equal To
catholicpriest
Nov 15, 2025 · 11 min read
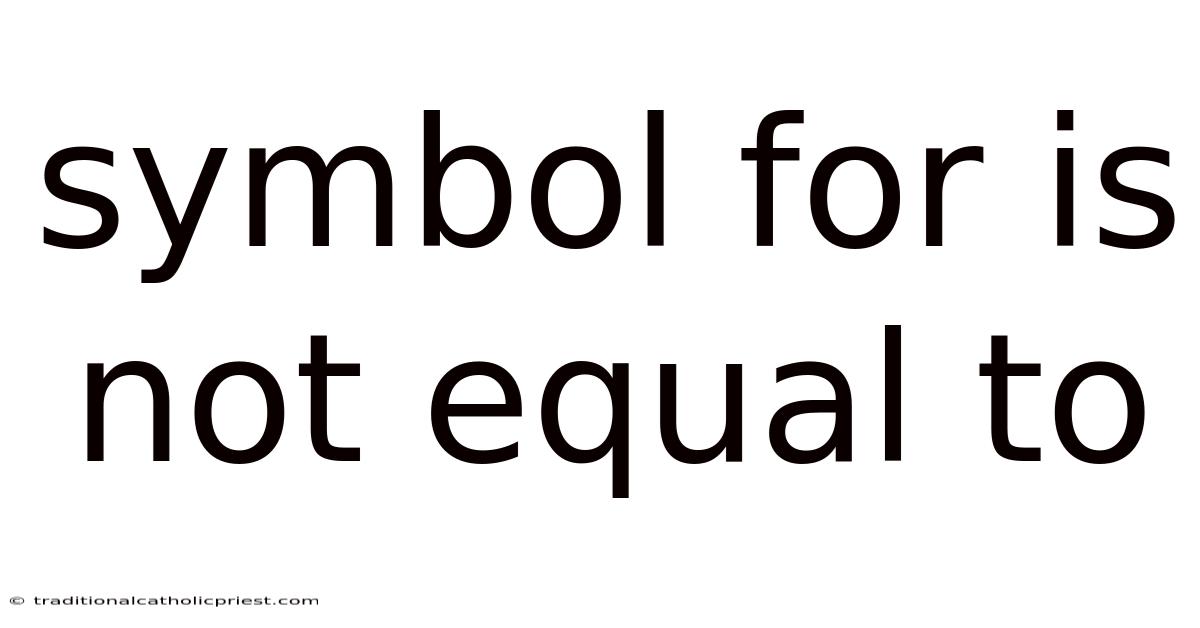
Table of Contents
Have you ever found yourself staring at a mathematical equation, knowing that two expressions aren't quite the same, but unsure how to properly convey that difference? Or perhaps you've been working on a programming project, needing a clear way to define when two variables do not hold identical values? This is where the "not equal to" symbol steps in as a precise tool, indispensable across mathematics, logic, and computer science.
Think of the equals sign (=) as representing perfect harmony and balance. The "not equal to" symbol, on the other hand, signals a break in that harmony, an assertion that things are distinct. It's a fundamental concept that underpins much of what we do in quantitative fields, allowing us to define conditions, express inequalities, and build systems that respond intelligently to varying inputs.
Main Subheading
The "not equal to" symbol, represented as ≠, is a mathematical symbol used to indicate that two values or expressions are not equal. This simple symbol is a cornerstone of mathematical notation, programming, and logical expressions. It serves as a clear and concise way to denote inequality, which is essential in many areas of quantitative analysis and problem-solving. Whether you're working with algebraic equations, conditional statements in programming, or logical propositions, understanding and using the "not equal to" symbol correctly is vital for accurate and effective communication.
The symbol itself is visually straightforward: an equals sign (=) with a slash (/) through it. This design directly conveys the concept of negation – that the equality normally implied by the equals sign is being denied. It's a universally recognized symbol, though its exact appearance may vary slightly depending on the font or context. Regardless of these minor variations, the meaning remains consistent. From handwritten notes to typeset textbooks, from lines of code to complex mathematical proofs, the "not equal to" symbol plays a crucial role in ensuring clarity and precision.
Comprehensive Overview
Definition and Symbolism
At its core, the "not equal to" symbol (≠) is a binary operator. It compares two values and asserts whether they are different. If a ≠ b, this statement means that a and b represent different quantities or expressions. The power of this symbol lies in its simplicity and directness. It doesn't require lengthy explanations or complex phrasing; it gets straight to the point in communicating a fundamental inequality.
The history of mathematical notation reveals that the equals sign (=) itself was popularized by Robert Recorde in 1557. The "not equal to" symbol likely emerged later as a natural extension, representing the opposite concept. While the exact origin is less clearly documented, its adoption reflects the need for a complete and consistent system of mathematical symbols. The slash through the equals sign visually signifies negation, a common theme in mathematical notation, also seen in symbols like ¬ for "not" in logic.
Use in Mathematics
In mathematics, the "not equal to" symbol is essential for several key areas:
- Algebra: When solving equations, you may encounter solutions where a variable cannot take on a specific value. For example, when dividing by an expression, you must specify that the expression cannot equal zero. In these cases, the "not equal to" symbol is critical.
- Inequalities: While symbols like < (less than) and > (greater than) define a specific ordering of values, the ≠ symbol simply states that two values are different, without specifying which is larger or smaller.
- Set Theory: In set theory, you might use the "not equal to" symbol to indicate that two sets are not identical, meaning they do not contain precisely the same elements.
- Calculus: When dealing with limits and continuity, you might use the "not equal to" symbol to define conditions where a function is undefined or discontinuous at a particular point.
Use in Computer Science
The "not equal to" symbol is equally important in computer science and programming. It is used extensively in conditional statements and logical operations to control the flow of programs based on whether two values are different.
- Programming Languages: Most programming languages provide a specific operator for "not equal to." Common examples include
!=in languages like C++, Java, and Python, and<>in SQL. - Conditional Statements: The "not equal to" operator is crucial in
ifstatements,whileloops, and other control structures. These statements allow a program to execute different blocks of code based on whether a condition involving inequality is met. - Data Validation: In data processing and validation, the "not equal to" symbol is used to ensure that data meets certain criteria. For instance, you might check if a user-entered value is not equal to a prohibited value.
- Database Queries: In SQL, the
<>or!=operator is used to filter records based on inequality. For example, you might select all customers whose city is not equal to "New York."
Logical Foundations
The "not equal to" symbol also has deep roots in logic. It's related to the concept of negation and the logical operator exclusive or (XOR). In propositional logic, if p represents the statement "a = b", then ¬p represents the statement "a ≠ b". This logical negation is a fundamental building block for complex logical arguments and proofs.
The XOR operation is also closely tied to the "not equal to" symbol. XOR returns true if and only if its two operands are different. In other words, XOR(a, b) is true if and only if a ≠ b. This connection to logic highlights the broader significance of the "not equal to" symbol as a means of expressing difference and distinction.
Practical Examples
To further illustrate the use of the "not equal to" symbol, consider the following examples:
-
Mathematics:
- If x² - 4 = 0, then x ≠ 1. (Because x can be 2 or -2)
- The set of all real numbers except 0 can be expressed as {x ∈ ℝ | x ≠ 0}.
-
Programming (Python):
x = 5 y = 10 if x != y: print("x and y are not equal") -
SQL:
SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE Department <> 'Sales';This query retrieves all employees who do not work in the Sales department.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the "not equal to" symbol itself is a well-established convention, its usage continues to evolve within the context of broader trends in mathematics, computer science, and data analysis. One notable trend is the increasing emphasis on data types and type safety in programming languages. Modern languages often provide mechanisms to ensure that comparisons are only performed between compatible types, reducing the risk of unexpected behavior when using the "not equal to" operator.
Another significant development is the rise of machine learning and artificial intelligence. In these fields, the "not equal to" symbol is used extensively in defining loss functions and evaluation metrics. For example, in classification problems, you might use the "not equal to" symbol to compare predicted labels with actual labels, assessing the accuracy of a model.
Furthermore, the increasing use of formal methods and automated theorem proving has led to a more rigorous treatment of mathematical notation, including the "not equal to" symbol. These tools provide a way to verify the correctness of mathematical statements and algorithms, ensuring that the "not equal to" symbol is used consistently and accurately.
From a professional perspective, understanding the nuances of the "not equal to" symbol is essential for anyone working in quantitative fields. Whether you're a software engineer, a data scientist, a mathematician, or a financial analyst, the ability to express and reason about inequality is a fundamental skill. Staying up-to-date with the latest developments in programming languages, data analysis techniques, and formal methods will help you use the "not equal to" symbol more effectively in your work.
Tips and Expert Advice
Mastering the use of the "not equal to" symbol can significantly enhance your problem-solving skills. Here are some practical tips and expert advice to help you use it effectively:
-
Understand the Context: Always consider the context in which you are using the "not equal to" symbol. In mathematics, this might involve understanding the domain of variables or the properties of sets. In programming, it might involve understanding the data types of variables or the specific requirements of an algorithm. Failing to consider the context can lead to errors and misinterpretations. For example, comparing a string to an integer using the "not equal to" operator might produce unexpected results if the programming language doesn't handle type conversions properly.
-
Be Precise with Data Types: In programming, pay close attention to data types when using the "not equal to" operator. Different data types have different comparison rules, and comparing incompatible types can lead to unexpected behavior. For example, in some languages, comparing a floating-point number to an integer might involve implicit type conversions, which can introduce rounding errors. To avoid these issues, it's best to ensure that you are comparing values of the same data type or explicitly convert them if necessary.
-
Use Parentheses for Clarity: When using the "not equal to" symbol in complex expressions, use parentheses to clarify the order of operations. This is especially important when combining the "not equal to" operator with other logical operators such as AND, OR, and NOT. Parentheses can help prevent ambiguity and ensure that the expression is evaluated correctly. For example, the expression
(a != b) && (c == d)clearly indicates that you are checking if a is not equal to b AND c is equal to d. -
Test Your Code Thoroughly: When using the "not equal to" operator in programming, always test your code thoroughly to ensure that it behaves as expected. Write unit tests to cover different scenarios and edge cases. This will help you identify and fix any errors related to inequality comparisons. For example, you might test your code with different input values, including boundary values and invalid inputs, to ensure that it handles them correctly.
-
Be Aware of Floating-Point Precision: When working with floating-point numbers, be aware of the limitations of floating-point precision. Due to the way floating-point numbers are represented in computers, small rounding errors can occur. This can lead to unexpected results when comparing floating-point numbers for equality or inequality. Instead of using the "not equal to" operator directly, it's often better to check if the absolute difference between two floating-point numbers is less than a small tolerance value. For example:
a = 1.0 / 3.0 b = 0.33333333333 tolerance = 1e-9 if abs(a - b) > tolerance: print("a and b are not approximately equal") -
Leverage Code Linters and Static Analysis Tools: Modern code linters and static analysis tools can detect potential issues with your code, including incorrect uses of the "not equal to" operator. Configure your development environment to use these tools and pay attention to any warnings or errors they report. This can help you catch subtle bugs early in the development process.
By following these tips and seeking expert advice, you can master the use of the "not equal to" symbol and improve your problem-solving skills in mathematics, computer science, and related fields.
FAQ
Q: Is there a difference between != and <>?
A: In most contexts, != and <> are interchangeable and both represent the "not equal to" operator. However, the specific syntax may vary depending on the programming language or database system you are using. For example, != is commonly used in languages like C++, Java, and Python, while <> is often used in SQL.
Q: How do I use "not equal to" in Excel?
A: In Excel, you can use the <> operator to represent "not equal to" in formulas and conditional formatting. For example, the formula =IF(A1<>B1, "Different", "Same") will display "Different" if the value in cell A1 is not equal to the value in cell B1, and "Same" otherwise.
Q: Can the "not equal to" symbol be used with strings?
A: Yes, the "not equal to" symbol can be used with strings to compare whether two strings are different. The comparison is typically case-sensitive, meaning that "Hello" and "hello" would be considered different.
Q: Is "not equal to" the same as "greater than or less than"?
A: No, "not equal to" is not the same as "greater than or less than." The "not equal to" symbol simply indicates that two values are different, without specifying which one is larger or smaller. "Greater than or less than" implies a specific ordering of values.
Q: How does the "not equal to" operator handle null values in SQL?
A: In SQL, comparing a column to a specific value with != or <> will not return rows where that column contains a null value. To specifically search for non-null values, you must use WHERE column IS NOT NULL. To find values that are not a specific value and also exclude nulls, you would combine these: WHERE column <> 'specific_value' AND column IS NOT NULL.
Conclusion
The "not equal to" symbol (≠) is a fundamental tool in mathematics, computer science, and logic. Its simple yet powerful function allows us to express inequality, define conditions, and build systems that respond to varying inputs. From algebraic equations to conditional statements in programming, the "not equal to" symbol plays a crucial role in ensuring clarity and precision.
By understanding its definition, applications, and nuances, you can significantly enhance your problem-solving skills and communicate effectively in quantitative fields. Remember to consider the context, be precise with data types, and test your code thoroughly when using the "not equal to" operator.
Now that you have a solid understanding of the "not equal to" symbol, put your knowledge into practice! Try using it in your next programming project, mathematical equation, or logical argument. Share your experiences and insights in the comments below, and let's continue to explore the fascinating world of mathematical notation together.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
1 2 Minus 1 3 In Fraction Form
Nov 15, 2025
-
The Angles Of A Triangle Add Up To
Nov 15, 2025
-
What Does The Gradient Of A Function Represent
Nov 15, 2025
-
How Does A Helicopter Fly Physics
Nov 15, 2025
-
What Does 1 Decimal Place Mean
Nov 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Symbol For Is Not Equal To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.