How Many Mm In 2 M
catholicpriest
Nov 22, 2025 · 12 min read
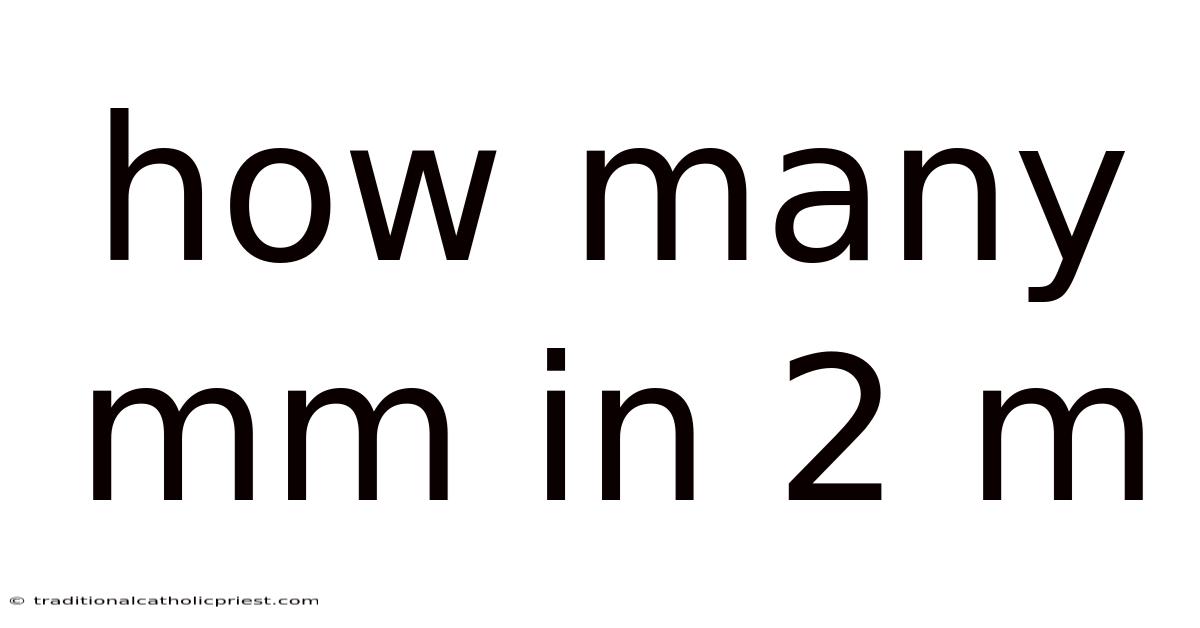
Table of Contents
Have you ever been in a situation where a slight miscalculation turned a simple task into a frustrating puzzle? Imagine fitting furniture into a room, only to find out that the measurements were off. Or perhaps you were following a recipe that demanded precise ingredient quantities. The world around us is built on measurements, and understanding how different units relate to each other is crucial for everything from home improvement to scientific research.
Converting between units, like millimeters and meters, is a fundamental skill that bridges these gaps. It’s not just about knowing the conversion factor; it’s about grasping the relationship between different scales of measurement. So, how many mm in 2 m? The answer is straightforward: there are 2,000 millimeters in 2 meters. But the real value lies in understanding why and how we arrive at this answer, and how this knowledge applies to everyday situations.
Understanding the Basics: Meters and Millimeters
To fully grasp the conversion between meters and millimeters, we first need to understand what each unit represents and how they fit into the broader metric system. The metric system, known for its simplicity and decimal-based structure, is the foundation for much of the world's measurements, especially in scientific and technical fields.
A meter (m) is the base unit of length in the metric system. Originally defined in terms of the Earth's circumference, it is now defined more precisely in terms of the speed of light. Think of a meter as roughly the height of a doorknob from the floor, or a little longer than a yardstick. It provides a practical and relatable scale for measuring distances and dimensions in everyday life.
A millimeter (mm), on the other hand, is a much smaller unit. The prefix milli- indicates one-thousandth, meaning that a millimeter is one-thousandth of a meter. To put it in perspective, a millimeter is about the thickness of a credit card or the width of a staple. This unit is essential for precise measurements in fields like engineering, manufacturing, and medicine, where accuracy is paramount.
The relationship between these units is simple but crucial: 1 meter is equal to 1,000 millimeters. This decimal-based relationship makes conversions straightforward. Understanding this foundation allows us to easily convert between these units and apply this knowledge in various practical contexts.
A Brief History of Measurement
The need for standardized measurement systems dates back to ancient civilizations. The Egyptians, for instance, used the cubit, the length from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger, as a standard unit. However, the problem with such systems was their variability; everyone's cubit is a different length! This inconsistency led to confusion and hindered trade and construction.
The metric system emerged from the French Revolution in the late 18th century, driven by the desire for a rational, universal system of measurement. In 1799, France officially adopted the meter as its standard unit of length. The meter was initially defined as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a meridian. This definition was groundbreaking because it was based on a natural constant, making it universally accessible.
Over time, the metric system gained popularity and was adopted by many countries due to its simplicity and ease of use. The decimal-based structure, where units are related by powers of ten, made calculations much easier compared to traditional systems. In 1875, the Treaty of the Meter was signed, establishing the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) to maintain and promote the metric system internationally.
Today, the metric system is the dominant system of measurement worldwide, used in science, industry, and everyday life. The United States remains one of the few countries that still primarily uses the imperial system (inches, feet, yards, miles), although the metric system is also used in many sectors, particularly in science and medicine. Understanding the history and evolution of measurement systems helps us appreciate the importance of standardization and the impact it has on global communication and collaboration.
The Math Behind the Conversion
The conversion from meters to millimeters is based on a simple mathematical relationship:
1 meter (m) = 1,000 millimeters (mm)
To convert any measurement from meters to millimeters, you simply multiply the number of meters by 1,000. So, to find out how many millimeters are in 2 meters, the calculation is as follows:
2 meters * 1,000 millimeters/meter = 2,000 millimeters
This straightforward multiplication provides the answer: there are 2,000 millimeters in 2 meters. This conversion factor is constant and universally applicable, making it easy to perform the calculation regardless of the context.
For example, if you have a length of 5 meters and you need to convert it to millimeters, you would multiply 5 by 1,000, resulting in 5,000 millimeters. Similarly, if you have 0.5 meters (half a meter), multiplying by 1,000 gives you 500 millimeters.
Understanding this simple multiplication rule allows for quick and accurate conversions, whether you're working on a DIY project, interpreting technical specifications, or simply trying to understand measurements in your daily life. This mathematical relationship is the key to effortlessly switching between these two units of length.
Real-World Applications
The ability to convert between meters and millimeters is incredibly useful in various real-world scenarios. Here are a few examples where this conversion becomes essential:
-
Construction and Carpentry: In construction, precision is key. When cutting materials like wood or metal, builders often need to switch between meters for larger dimensions and millimeters for detailed work. For instance, a blueprint might specify the length of a wall in meters, but the thickness of a wooden board in millimeters. Knowing that there are 2,000 mm in 2 m allows carpenters to accurately cut materials to fit specific designs, ensuring structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Engineers frequently work with very precise measurements. Designing components for machines or electronic devices often requires measurements in millimeters to ensure parts fit together perfectly. If a mechanical engineer is designing a part that needs to be 2 meters long, they'll need to know that this is equivalent to 2,000 millimeters to ensure the part is manufactured to the correct specifications.
-
Medical Field: In medicine, accuracy can be a matter of life and death. Medical devices, implants, and even dosages often require precise measurements in millimeters. For example, a surgeon planning an incision or implanting a device needs to know exact dimensions to avoid complications. If a medical device is designed to be 2 meters in length for a specific procedure, healthcare professionals must be able to accurately convert this to 2,000 millimeters to verify it meets the necessary specifications.
-
DIY Projects and Home Improvement: Many home improvement projects require converting between meters and millimeters. Whether you're installing flooring, building shelves, or fitting furniture, accurate measurements are essential for a successful outcome. Imagine you're installing a 2-meter-long countertop. Knowing that this is equal to 2,000 millimeters helps you to accurately measure and cut the countertop to fit perfectly within your kitchen.
-
Photography: Photographers often deal with lens measurements in millimeters. The focal length of a lens, for example, is measured in millimeters and affects the field of view and magnification. Understanding this unit helps photographers choose the right lens for different types of shots, whether it's a wide-angle landscape or a detailed close-up.
In each of these situations, the ability to quickly and accurately convert between meters and millimeters is crucial for precision, safety, and success.
Current Trends in Measurement
The world of measurement is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the increasing demand for precision. Here are some current trends and developments in the field:
-
Digital Measurement Tools: Traditional measuring tapes and rulers are being replaced by digital tools that offer greater accuracy and convenience. Laser distance meters, for example, can measure distances up to hundreds of meters with millimeter accuracy, making them ideal for construction, surveying, and real estate. These tools often come with features like data logging, Bluetooth connectivity, and integration with CAD software, enhancing productivity and reducing errors.
-
3D Scanning and Measurement: 3D scanning technology is revolutionizing industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and archaeology. 3D scanners can capture the shape and dimensions of objects with incredible precision, creating detailed digital models that can be used for analysis, replication, or customization. These scanners often measure in millimeters or even micrometers, allowing for highly accurate representations of physical objects.
-
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Sensors: The IoT is connecting devices and systems in unprecedented ways, generating vast amounts of data about the physical world. Sensors play a crucial role in this ecosystem, measuring everything from temperature and pressure to distance and velocity. These sensors often provide data in metric units, including millimeters, which can be used for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
-
Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM is a digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility. It's used extensively in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. BIM models incorporate precise measurements in both meters and millimeters, allowing stakeholders to visualize, simulate, and analyze construction projects before they even break ground. This leads to better coordination, reduced costs, and improved project outcomes.
-
Standardization and Metrology: As technology advances, the need for standardized measurement practices and metrology (the science of measurement) becomes even more critical. Organizations like the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) play a key role in maintaining and promoting measurement standards, ensuring that measurements are accurate, consistent, and traceable across different industries and countries.
These trends highlight the increasing importance of accurate and reliable measurements in a wide range of fields. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated measurement tools and techniques to emerge, further transforming the way we interact with the physical world.
Expert Tips for Accurate Conversions
Converting between meters and millimeters is straightforward, but here are some expert tips to ensure accuracy and avoid common mistakes:
-
Double-Check Your Work: Always double-check your calculations, especially when dealing with critical measurements. A simple error can lead to significant problems in construction, engineering, or medicine. Use a calculator or online conversion tool to verify your results and catch any potential mistakes.
-
Use Consistent Units: When working on a project, make sure to use consistent units throughout. Switching back and forth between meters and millimeters can increase the risk of errors. Choose one unit of measurement and stick with it as much as possible. If you need to convert, do it at the beginning of the project to avoid confusion later on.
-
Understand Significant Figures: Be mindful of significant figures, especially when working with precise measurements. Significant figures indicate the precision of a measurement and should be preserved during conversions and calculations. For example, if you have a measurement of 2.0 meters, it implies a higher level of precision than a measurement of 2 meters.
-
Use Digital Tools Wisely: Digital measurement tools like laser distance meters and online converters can be incredibly helpful, but they are not foolproof. Always calibrate your tools according to the manufacturer's instructions and be aware of their limitations. Don't rely solely on digital tools; use your judgment and common sense to verify the results.
-
Practice Regularly: Like any skill, converting between meters and millimeters becomes easier with practice. Regularly perform conversions in your daily life, whether you're measuring furniture, following a recipe, or working on a DIY project. The more you practice, the more confident and accurate you'll become.
-
Understand the Context: Consider the context of the measurement. In some situations, a rough estimate may be sufficient, while in others, extreme precision is required. For example, when estimating the length of a room, a few millimeters of error may not matter. However, when manufacturing a critical component for an aircraft, even a tiny error can have serious consequences.
By following these expert tips, you can ensure accurate conversions and avoid costly mistakes. Accurate measurements are essential for success in many fields, so taking the time to master this skill is well worth the effort.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why is it important to know how to convert meters to millimeters?
A: Converting meters to millimeters is essential for precision in various fields like construction, engineering, medicine, and DIY projects. Accurate conversions ensure that designs, measurements, and implementations are correct, preventing errors and ensuring safety.
Q: Is there a simple way to remember the conversion factor?
A: Yes, remember that milli- means one-thousandth. Therefore, 1 meter equals 1,000 millimeters. To convert from meters to millimeters, you simply multiply by 1,000.
Q: Can I use an online tool to convert meters to millimeters?
A: Absolutely! Many online conversion tools are available for quick and accurate conversions. Just enter the value in meters, and the tool will instantly provide the equivalent in millimeters. However, always double-check the result to ensure accuracy.
Q: What is the difference between a millimeter and a micrometer?
A: A millimeter is one-thousandth of a meter (1/1,000 m), while a micrometer is one-millionth of a meter (1/1,000,000 m). A micrometer is 1,000 times smaller than a millimeter.
Q: In which industries is millimeter precision most critical?
A: Millimeter precision is most critical in industries such as aerospace, microelectronics, precision manufacturing, and microsurgery, where even the slightest error can have significant consequences.
Conclusion
Understanding how to convert between meters and millimeters is more than just a mathematical exercise; it's a practical skill that impacts numerous aspects of our lives. Knowing that there are 2,000 mm in 2 m provides a foundational understanding of measurement that applies to everything from home improvement to professional engineering. By grasping the underlying principles, utilizing reliable conversion methods, and appreciating the real-world applications, you can confidently navigate measurements in any situation.
Now that you have a solid understanding of meters and millimeters, put your knowledge into practice! Whether you're planning a DIY project, assisting with a school assignment, or simply curious about the world around you, take the opportunity to apply your newfound skills. Explore different measurement tools, experiment with conversions, and challenge yourself to think in metric. And if you found this article helpful, share it with others who might benefit from a clearer understanding of metric conversions. Let's build a world where accurate measurement empowers everyone.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Mm In 2 M . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.