F Of X Plus G Of X
catholicpriest
Nov 29, 2025 · 14 min read
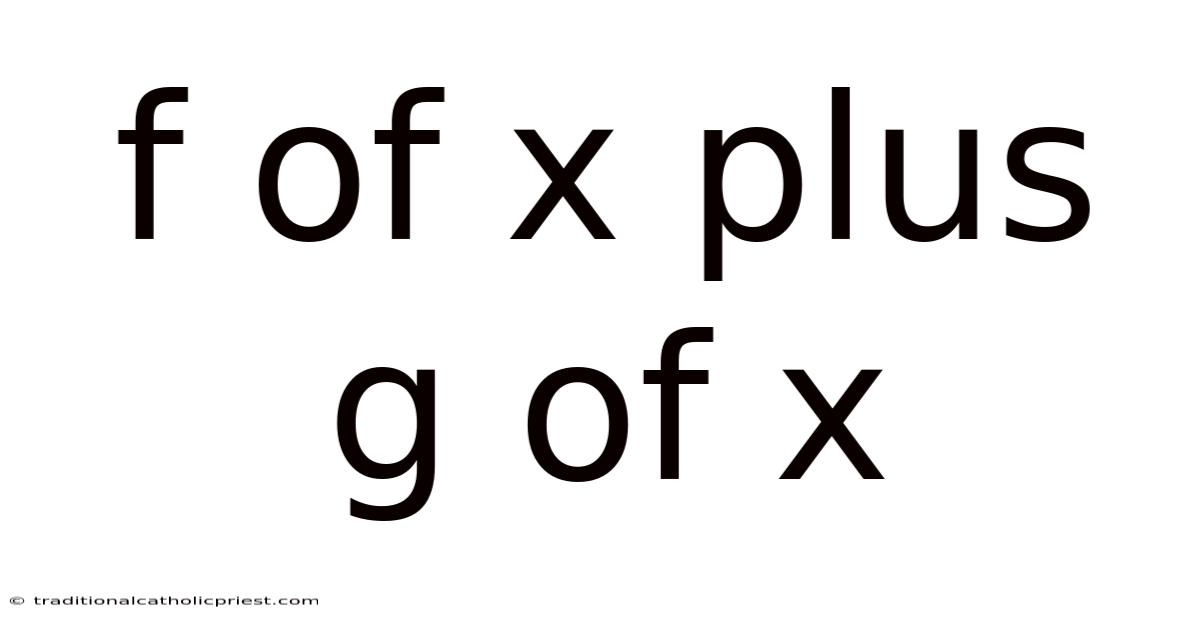
Table of Contents
Imagine you're baking a cake. You have two recipes: one for the cake itself, let's call it recipe "f," and another for the frosting, recipe "g." Each recipe requires specific ingredients and steps to create its delicious outcome. But what if you wanted to combine the best of both worlds – the cake and the frosting together? In mathematics, a similar concept exists when we talk about "f of x plus g of x," it's like adding the two recipes together to get a final, combined dessert.
The idea of combining functions like "f of x plus g of x" is a fundamental operation in mathematics with a wide range of applications, from physics and engineering to economics and computer science. Understanding how to perform this operation, its rules, and its implications is crucial for anyone working with mathematical models. Whether you are a student grappling with algebra or a professional using advanced calculus, mastering the concept of function addition will undoubtedly enhance your analytical toolkit. Let’s explore this concept in detail, uncovering its nuances and practical uses.
Main Subheading: Understanding the Basics of Function Addition
In mathematics, functions are relationships between two sets of elements. These sets are usually called the domain and the range. Think of a function as a machine: you put something in (an input from the domain), and the machine gives you something back (an output in the range). When we talk about "f of x," written as f(x), we're describing a specific function named "f" that takes "x" as an input. Similarly, g(x) represents another function named "g" taking "x" as its input.
The operation "f of x plus g of x," written as f(x) + g(x), simply means adding the outputs of the two functions f(x) and g(x) for the same input value "x." It's like having two different machines, f and g, both processing the same input "x," and then adding their results together. This combined result forms a new function, often denoted as h(x) = f(x) + g(x).
Consider a simple example: Let's say f(x) = x² and g(x) = 2x. To find f(x) + g(x), we simply add the expressions together: h(x) = f(x) + g(x) = x² + 2x
So, for any value of "x," the output of the new function h(x) is the sum of x² and 2x. For instance, if x = 3, then: f(3) = 3² = 9 g(3) = 2 * 3 = 6 h(3) = f(3) + g(3) = 9 + 6 = 15
Comprehensive Overview: Delving Deeper into Function Addition
To truly understand the concept of f(x) + g(x), we need to explore the formal definition, the underlying principles, and some critical considerations. Let's dive deeper into each of these aspects.
Formal Definition
Formally, if f and g are two functions with overlapping domains, then the sum of f and g, denoted as f + g, is a new function defined by: (f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x) The domain of f + g is the intersection of the domains of f and g. This means that x must be a valid input for both f(x) and g(x) for the addition to be defined.
Domain Considerations
The domain of the resulting function h(x) = f(x) + g(x) is a critical aspect to consider. Since we are adding the outputs of f(x) and g(x), the input "x" must be valid for both functions. This means that the domain of h(x) is the intersection of the domains of f(x) and g(x). For example, if f(x) = √(x) and g(x) = 1/(x - 1):
- The domain of f(x) is x ≥ 0 (since we can only take the square root of non-negative numbers).
- The domain of g(x) is x ≠ 1 (since we cannot divide by zero).
- Therefore, the domain of f(x) + g(x) is x ≥ 0 and x ≠ 1.
Graphical Interpretation
Function addition can also be visualized graphically. If you have the graphs of f(x) and g(x), you can obtain the graph of f(x) + g(x) by adding the y-values of f(x) and g(x) for each value of x. Imagine plotting both f(x) and g(x) on the same coordinate plane. For each x-value, measure the vertical distance from the x-axis to the graph of f(x) and then add it to the vertical distance from the x-axis to the graph of g(x). The resulting sum gives you the y-value of the new function f(x) + g(x) at that x-value. This process can be repeated for several x-values to plot the entire graph of f(x) + g(x).
Properties of Function Addition
Function addition shares several properties with regular addition of numbers. These properties can be useful when simplifying expressions or solving equations involving function addition:
- Commutative Property: f(x) + g(x) = g(x) + f(x). The order in which you add the functions does not matter.
- Associative Property: (f(x) + g(x)) + h(x) = f(x) + (g(x) + h(x)). When adding more than two functions, the grouping does not matter.
- Identity Property: There exists an identity function z(x) = 0 such that f(x) + z(x) = f(x). Adding the zero function does not change the original function.
Applications in Modeling
Function addition is a fundamental tool in mathematical modeling. It allows us to combine different aspects of a system into a single, comprehensive model. For example:
- Physics: In physics, you might use function addition to model the total force acting on an object as the sum of individual forces. If f(x) represents the force due to gravity and g(x) represents the force due to air resistance, then f(x) + g(x) represents the total force acting on the object.
- Economics: In economics, you might model the total cost of production as the sum of fixed costs and variable costs. If f(x) represents the fixed costs and g(x) represents the variable costs as a function of quantity x, then f(x) + g(x) represents the total cost of producing x units.
- Engineering: In signal processing, function addition is used to combine different signals. If f(t) represents one signal and g(t) represents another signal, then f(t) + g(t) represents the combined signal.
Trends and Latest Developments
The concept of adding functions is not just a theoretical idea; it's actively used in many cutting-edge fields and research areas. Here are some notable trends and recent developments:
Machine Learning and Neural Networks
In machine learning, especially in the architecture of neural networks, the addition of functions plays a crucial role. Neural networks are built from layers of interconnected nodes, and each node applies a function to its input. The outputs of these functions are then often summed before being passed to the next layer. This process allows the network to learn complex patterns by combining simpler functions. Deep Learning: In deep learning models, complex transformations are achieved through successive additions and compositions of simpler functions. Residual networks (ResNets), for example, use "skip connections" that add the input of a layer to its output, facilitating the training of very deep networks.
Signal Processing and Data Analysis
Signal processing relies heavily on function addition for tasks like noise reduction and signal enhancement. By adding or superimposing different signals, unwanted components can be filtered out, or desired components can be amplified. Applications: This is used extensively in audio processing, image processing, and telecommunications, where signals are often represented as functions.
Financial Modeling
In financial modeling, adding functions is essential for creating comprehensive models of market behavior. Different factors affecting stock prices, interest rates, or economic indicators can be modeled as separate functions and then added together to forecast future trends. Example: One might add a function representing the effect of interest rates on stock prices to another function representing the impact of company earnings.
Control Systems
Control systems engineering uses function addition to analyze and design systems that regulate various processes. By adding different control signals and feedback loops, engineers can optimize the performance of systems ranging from aircraft autopilots to industrial process controllers.
Functional Analysis and Operator Theory
At a more abstract level, in the field of functional analysis, the addition of functions is studied in the context of vector spaces of functions. This leads to the development of powerful tools and theorems that are used in many areas of mathematics and physics.
Insight: The study of linear operators, which are functions that map functions to other functions while preserving addition and scalar multiplication, is a central theme in this area.
Professional Insights
- Interdisciplinary Applications: Professionals across various disciplines leverage function addition to build integrated models and gain deeper insights into complex phenomena.
- Computational Tools: With the advent of sophisticated computational tools and software packages (like MATLAB, Python with NumPy, and R), the practical application of function addition has become more accessible and efficient.
- Model Complexity: While adding functions can enhance the completeness of a model, it's important to manage complexity. Overly complex models can be difficult to interpret and may suffer from overfitting issues, particularly in machine learning contexts.
- Data-Driven Approaches: The increasing availability of large datasets has enabled the creation of more accurate and nuanced models based on function addition. Data-driven approaches allow for empirical validation and refinement of these models, ensuring their relevance and applicability.
Tips and Expert Advice
Understanding function addition involves not only grasping the theoretical concepts but also knowing how to apply them effectively in practice. Here are some tips and expert advice to help you master this operation:
1. Understand Domain Restrictions
Always be mindful of the domains of the functions you are adding. The domain of the resulting function is the intersection of the domains of the individual functions. Failing to consider this can lead to incorrect or undefined results.
- Example: If f(x) = √(x - 2) and g(x) = 1/(x - 5), the domain of f is x ≥ 2, and the domain of g is x ≠ 5. Therefore, the domain of f(x) + g(x) is x ≥ 2 and x ≠ 5. Be sure to exclude x = 5 from your calculations.
- Tip: Graphing the functions can help visualize their domains and identify potential restrictions.
2. Simplify Expressions Before Adding
Before adding functions, simplify each expression as much as possible. This will make the addition process easier and reduce the chances of making errors.
- Example: Suppose f(x) = (x² + 2x + 1) / (x + 1) and g(x) = x - 3. First, simplify f(x) to x + 1. Then, f(x) + g(x) = (x + 1) + (x - 3) = 2x - 2.
- Tip: Look for opportunities to factor, cancel terms, or combine like terms within each function before adding them.
3. Use Graphical Analysis for Visualization
Graphs can provide valuable insights into the behavior of functions and their sums. Use graphing tools or software to visualize f(x), g(x), and f(x) + g(x).
- Example: By plotting f(x) and g(x), you can visually confirm the domain restrictions and see how the y-values combine to form the graph of f(x) + g(x).
- Tip: Pay attention to how the graphs of f(x) and g(x) interact. Notice where one function dominates the sum and where they contribute equally.
4. Practice with Different Types of Functions
To become proficient with function addition, practice with a variety of function types, including polynomials, trigonometric functions, exponential functions, and logarithmic functions.
- Example: Try adding f(x) = sin(x) and g(x) = cos(x), or f(x) = e^x and g(x) = x².
- Tip: Familiarize yourself with the properties and characteristics of each type of function to better understand how they behave when added together.
5. Apply Function Addition to Real-World Problems
To solidify your understanding, apply function addition to real-world problems in fields like physics, engineering, economics, and computer science.
- Example: Model the total cost of a business as the sum of fixed costs and variable costs, or model the total force acting on an object as the sum of individual forces.
- Tip: Look for opportunities to break down complex problems into simpler components that can be represented as functions.
6. Utilize Technology and Software
Take advantage of technology and software tools to perform function addition and analysis. Tools like graphing calculators, computer algebra systems (CAS), and programming languages can simplify the process and provide accurate results.
- Example: Use MATLAB, Python with NumPy, or Mathematica to define functions and perform addition operations.
- Tip: Learn how to use these tools effectively to visualize functions, solve equations, and perform simulations.
7. Check Your Work and Verify Results
Always check your work and verify your results. Use different methods to confirm your answers, such as substituting values, graphing functions, or using computational tools.
- Example: After adding two functions, substitute a few values of x into f(x), g(x), and f(x) + g(x) to ensure that the sum is correct.
- Tip: Develop a habit of double-checking your work to avoid errors and build confidence in your abilities.
8. Collaborate and Seek Feedback
Collaborate with peers and seek feedback from instructors or mentors. Discussing problems and solutions with others can help you gain new insights and improve your understanding.
- Example: Work through practice problems with a study group and compare your approaches and solutions.
- Tip: Be open to constructive criticism and use feedback to identify areas for improvement.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What does "f of x plus g of x" mean? A: "f of x plus g of x," written as f(x) + g(x), means adding the outputs of the two functions f(x) and g(x) for the same input value x. It results in a new function where each output is the sum of the corresponding outputs of f(x) and g(x).
Q: How do I find the domain of f(x) + g(x)? A: The domain of f(x) + g(x) is the intersection of the domains of f(x) and g(x). This means that x must be a valid input for both f(x) and g(x) for the addition to be defined.
Q: Can I add any two functions together? A: You can add any two functions together as long as they have overlapping domains. If their domains do not overlap, then the sum f(x) + g(x) is not defined for any x.
Q: Is f(x) + g(x) the same as f(x) * g(x)? A: No, f(x) + g(x) represents the sum of the outputs of f(x) and g(x), while f(x) * g(x) represents the product of their outputs. These are two different operations.
Q: What are some real-world applications of function addition? A: Function addition is used in various fields, including physics (to model total forces), economics (to model total costs), engineering (in signal processing), and computer science (in machine learning).
Q: What if one of the functions is a constant? A: If one of the functions is a constant, say g(x) = c, then f(x) + g(x) = f(x) + c. This simply means adding the constant value c to the output of the function f(x) for every value of x.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of f(x) + g(x) is crucial for anyone delving into mathematics, science, or engineering. It's a fundamental operation that allows us to combine different mathematical models and analyze complex systems. By grasping the definitions, domain considerations, graphical interpretations, and practical applications, you can confidently apply function addition to solve a wide range of problems. Always remember to consider the domains of the functions, simplify expressions before adding, and visualize the results graphically to gain deeper insights.
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of f(x) + g(x), it's time to put your knowledge into practice. Try working through some practice problems, exploring different types of functions, and applying function addition to real-world scenarios. Don't hesitate to seek help or collaborate with others if you encounter difficulties. Share this article with your friends or colleagues and start a discussion about how you can apply this knowledge in your respective fields!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A 13 Sided Figure Called
Nov 29, 2025
-
How Do You Spell Months Of The Year
Nov 29, 2025
-
5 Letter Word Starting With Tor
Nov 29, 2025
-
The Market System Is An Economic System That
Nov 29, 2025
-
Three Letter Words That Begin With Q
Nov 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about F Of X Plus G Of X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.