A2 B2 C2 Solve For C
catholicpriest
Dec 06, 2025 · 12 min read
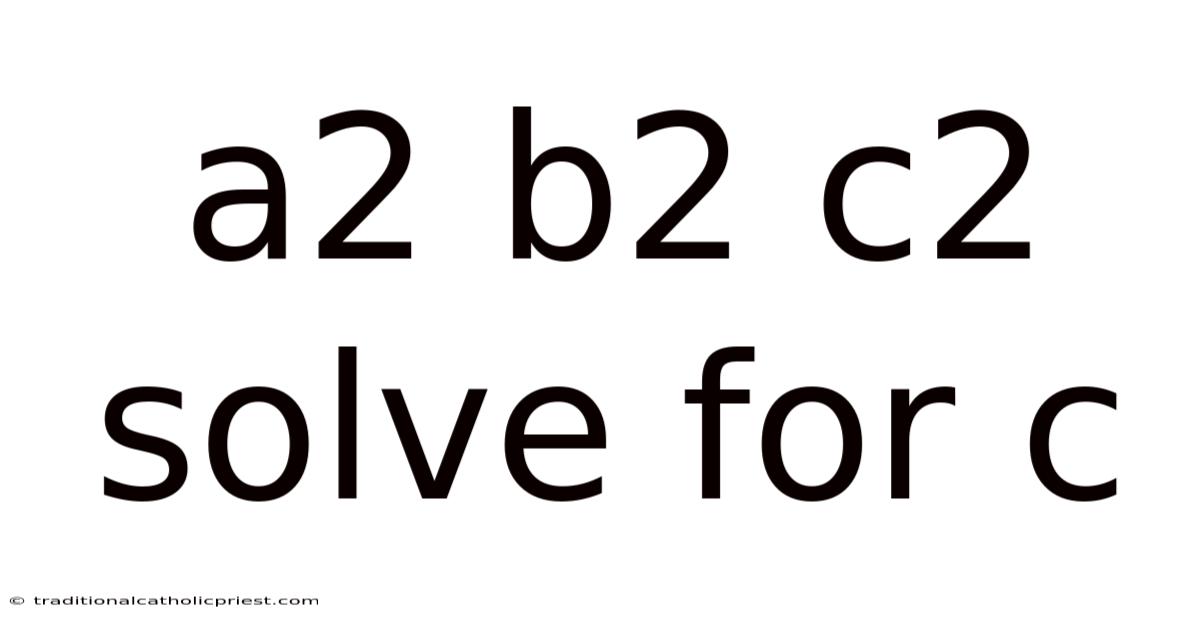
Table of Contents
Have you ever stared at a mathematical equation, feeling like you're deciphering an ancient code? Many of us have been there, especially when dealing with algebraic formulas. It’s like holding a map without knowing where ‘X’ marks the spot. Formulas can seem daunting, but when broken down into manageable steps, they become surprisingly accessible and even... dare I say... enjoyable?
Think about it: formulas are the languages through which scientists and mathematicians communicate universal truths. When we learn to manipulate them, we gain a new level of understanding about the world. Today, we're tackling a specific challenge: isolating 'c' in the equation a² + b² = c². This isn't just an abstract mathematical exercise; it's a cornerstone of many real-world applications, from calculating distances in navigation to understanding the fundamental relationships in physics and engineering. So, let's embark on this algebraic adventure together, turning that intimidating equation into a clear path to finding 'c'!
Unveiling the Equation: a² + b² = c²
The equation a² + b² = c² is not just any random assembly of letters and symbols; it’s the celebrated Pythagorean Theorem. This fundamental concept, deeply rooted in geometry, expresses the relationship between the sides of a right-angled triangle. It states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. Understanding this theorem is crucial for grasping numerous concepts in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
Before diving into the algebraic manipulation to solve for c, let’s establish a solid understanding of the theorem's components and its significance. The sides a and b are often referred to as the legs of the right triangle, while c represents the hypotenuse. The theorem provides a way to calculate the length of one side if the lengths of the other two are known. This is invaluable in many practical applications, such as construction, navigation, and even computer graphics.
Comprehensive Overview: The Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem, a² + b² = c², stands as a cornerstone of geometry, and its influence extends far beyond the classroom. To fully appreciate its power and utility, we need to delve into its historical roots, mathematical underpinnings, and broad applications.
Historical Context
The theorem is named after the ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras, who is credited with formalizing and popularizing it, although evidence suggests that the relationship was known to earlier civilizations, including the Babylonians and Egyptians. The Babylonians, for instance, used Pythagorean triples (sets of three positive integers that satisfy the theorem) in their calculations, indicating an understanding of the relationship long before Pythagoras. Regardless of its exact origin, Pythagoras and his followers were instrumental in bringing this concept into the realm of formal mathematics.
Mathematical Foundation
At its core, the Pythagorean Theorem describes a fundamental property of Euclidean space. It's based on the concept of distance and how it relates to the coordinates of points in a two-dimensional plane. Consider a right-angled triangle placed on a coordinate grid. The lengths of the sides a and b can be seen as the differences in the x and y coordinates, respectively, of the points defining the triangle. The hypotenuse c then represents the straight-line distance between those two points.
The theorem is more than just a formula; it’s a gateway to understanding deeper mathematical concepts. It links algebra and geometry, providing a bridge between numerical calculations and spatial relationships. This connection is crucial in fields like trigonometry, where the ratios of the sides of right triangles are used to define trigonometric functions.
Solving for c: The Hypotenuse
To solve for c in the equation a² + b² = c², we need to isolate c on one side of the equation. This involves taking the square root of both sides. Here’s the step-by-step process:
- Start with the equation: a² + b² = c²
- Take the square root of both sides: √(a² + b²) = √(c²)
- Simplify: √(a² + b²) = c
- Thus, c = √(a² + b²)
This formula allows us to find the length of the hypotenuse c when we know the lengths of the other two sides, a and b.
Applications in the Real World
The applications of the Pythagorean Theorem are vast and varied. In construction, it is used to ensure that buildings are square and structurally sound. By verifying that the sides of a foundation or a wall satisfy the theorem, builders can ensure right angles are precise. In navigation, the theorem is used to calculate distances and plan routes. For example, sailors and pilots can use it to determine the shortest distance between two points, taking into account their current position and destination.
In computer graphics, the Pythagorean Theorem is essential for rendering images and creating realistic simulations. It is used to calculate distances between points in 3D space, which is crucial for determining how objects appear on the screen. In physics, the theorem is used in mechanics to calculate resultant forces and velocities. For example, if two forces are acting on an object at right angles, the resultant force can be found using the Pythagorean Theorem.
Limitations and Extensions
While the Pythagorean Theorem is powerful, it is important to recognize its limitations. It applies only to right-angled triangles in Euclidean space. In non-Euclidean geometries, such as spherical or hyperbolic geometry, the relationship between the sides of a triangle is different. However, the theorem has been extended and generalized in various ways to apply to more general situations.
For example, the Law of Cosines is a generalization of the Pythagorean Theorem that applies to any triangle, not just right-angled ones. It states that c² = a² + b² - 2ab cos(γ), where γ is the angle between sides a and b. When γ is 90 degrees (a right angle), cos(γ) = 0, and the Law of Cosines reduces to the Pythagorean Theorem.
Trends and Latest Developments
The Pythagorean Theorem, while ancient, continues to be relevant in modern mathematics and its applications. Current trends involve leveraging its principles in new technologies and exploring its connections to advanced mathematical concepts.
One notable trend is the use of the Pythagorean Theorem in machine learning and data analysis. Algorithms for clustering, classification, and dimensionality reduction often rely on distance calculations, and the Pythagorean Theorem provides a fundamental way to compute these distances in multi-dimensional spaces. For example, in k-nearest neighbors (k-NN) algorithms, the distance between data points is a critical factor in determining their similarity, and the Pythagorean Theorem is used to calculate these distances efficiently.
Another area of development is the use of the Pythagorean Theorem in cryptography. Certain cryptographic algorithms rely on the difficulty of solving geometric problems in high-dimensional spaces, and the Pythagorean Theorem plays a role in defining these problems. For instance, lattice-based cryptography, which is considered a promising candidate for post-quantum cryptography, uses lattices in high-dimensional spaces, and the Pythagorean Theorem is used to calculate distances within these lattices.
Furthermore, the Pythagorean Theorem is being integrated into educational technology to enhance learning and understanding. Interactive software and simulations allow students to explore the theorem in dynamic and engaging ways, fostering a deeper appreciation for its geometric and algebraic properties. These tools often provide visual representations of right triangles, allowing students to manipulate the side lengths and observe how the theorem holds true in different scenarios.
From a professional perspective, the continued relevance of the Pythagorean Theorem highlights the importance of foundational mathematical knowledge in a wide range of fields. Engineers, scientists, and computer scientists all benefit from a solid understanding of this theorem and its applications. As technology advances and new challenges emerge, the Pythagorean Theorem will continue to serve as a valuable tool for solving problems and making new discoveries.
Tips and Expert Advice
Solving for c using the Pythagorean Theorem may seem straightforward, but mastering it requires attention to detail and a strategic approach. Here are some practical tips and expert advice to help you solve problems involving a² + b² = c² effectively:
-
Understand the Context: Before applying the theorem, make sure you are dealing with a right-angled triangle. The theorem only holds true for right triangles, where one angle is exactly 90 degrees. If you're working with a different type of triangle, you'll need to use the Law of Cosines or other trigonometric relationships. For example, in surveying, identifying right angles using tools like theodolites or laser levels ensures accurate measurements for applying the theorem.
-
Label the Sides Correctly: Ensure that you correctly identify the hypotenuse (c) and the other two sides (a and b). The hypotenuse is always the side opposite the right angle and is the longest side of the triangle. Mislabeling the sides can lead to incorrect calculations and inaccurate results. In construction, for instance, correctly identifying the hypotenuse is crucial when calculating roof slopes or diagonal bracing.
-
Use Consistent Units: When performing calculations, make sure all the sides are measured in the same units. If one side is in meters and another is in centimeters, convert them to the same unit before applying the theorem. Mixing units can lead to significant errors in your calculations. In architectural design, consistent units are essential when calculating room dimensions or structural components.
-
Simplify Radicals: After finding the value of c by taking the square root, simplify the radical expression if possible. This makes the answer easier to understand and work with. For example, if c = √50, simplify it to c = 5√2. In engineering applications, simplified radicals can streamline calculations and reduce the risk of errors.
-
Check Your Answer: Once you've calculated the value of c, check your answer to ensure it makes sense in the context of the problem. For example, the length of the hypotenuse should always be greater than the lengths of the other two sides. If your answer doesn't satisfy this condition, you've likely made an error in your calculations. In navigation, verifying that the calculated distance between two points is reasonable given the map scale can prevent costly mistakes.
-
Use Pythagorean Triples: Familiarize yourself with common Pythagorean triples, such as (3, 4, 5), (5, 12, 13), and (8, 15, 17). Recognizing these triples can help you quickly solve problems without having to go through the full calculation. For example, if you know that a = 3 and b = 4, you can immediately deduce that c = 5. In carpentry, using Pythagorean triples can simplify the process of cutting lumber to create right angles in frames and structures.
-
Apply Estimation Techniques: Before performing the calculations, estimate the value of c to get a sense of what the answer should be. This can help you catch errors and ensure that your final answer is reasonable. For example, if a = 6 and b = 8, estimate that c will be slightly larger than 8 but less than 10. In land surveying, estimating distances can help verify the accuracy of measurements and prevent significant errors in boundary determination.
-
Use Technology Wisely: While it's important to understand the underlying principles of the Pythagorean Theorem, don't hesitate to use technology to help with calculations. Calculators, spreadsheets, and specialized software can automate the process and reduce the risk of human error. However, be sure to double-check the results and understand how the technology is performing the calculations. In structural engineering, software tools can automate the process of calculating stresses and strains in complex structures using the Pythagorean Theorem and related principles.
FAQ
Q: What is the Pythagorean Theorem used for?
A: The Pythagorean Theorem is primarily used to find the length of an unknown side in a right-angled triangle when the lengths of the other two sides are known. It has wide applications in construction, navigation, engineering, and various other fields.
Q: Can the Pythagorean Theorem be used for non-right triangles?
A: No, the Pythagorean Theorem applies only to right-angled triangles. For non-right triangles, you need to use the Law of Cosines or the Law of Sines.
Q: What is a Pythagorean triple?
A: A Pythagorean triple is a set of three positive integers a, b, and c that satisfy the equation a² + b² = c². Common examples include (3, 4, 5), (5, 12, 13), and (8, 15, 17).
Q: How do I solve for a or b instead of c?
A: To solve for a, rearrange the equation as a² = c² - b², and then take the square root to get a = √(c² - b²). Similarly, to solve for b, rearrange the equation as b² = c² - a², and then take the square root to get b = √(c² - a²).
Q: What if I have more than two sides known?
A: The Pythagorean Theorem only requires two sides to be known to find the third side in a right-angled triangle. If you have more information, it can be used to verify the consistency of the data or solve related problems.
Conclusion
In summary, the equation a² + b² = c², known as the Pythagorean Theorem, is a fundamental principle in mathematics that allows us to find the length of the hypotenuse (c) in a right-angled triangle when the lengths of the other two sides (a and b) are known. Its applications span across various fields, from construction and navigation to computer graphics and physics, making it an essential tool for problem-solving and innovation. Understanding the theorem's history, mathematical foundation, and practical applications can empower you to tackle a wide range of challenges effectively.
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of the Pythagorean Theorem and how to solve for c, take the next step! Try applying this knowledge to real-world problems and explore its connections to other areas of mathematics and science. Share your insights and experiences in the comments below, and let's continue to learn and grow together. Are there any specific scenarios you've encountered where solving for 'c' using this theorem has been particularly useful or challenging? Share your stories – your experiences could help others grasp these concepts even more effectively!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Equation For The Axis Of Symmetry
Dec 06, 2025
-
Specific Heat Capacity Vs Heat Capacity
Dec 06, 2025
-
List All The Factors Of 45
Dec 06, 2025
-
5 Letter Words That Begin With C A
Dec 06, 2025
-
Five Letter Word Starting With As
Dec 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A2 B2 C2 Solve For C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.