30 Degree 30 Is Equal To
catholicpriest
Dec 06, 2025 · 10 min read
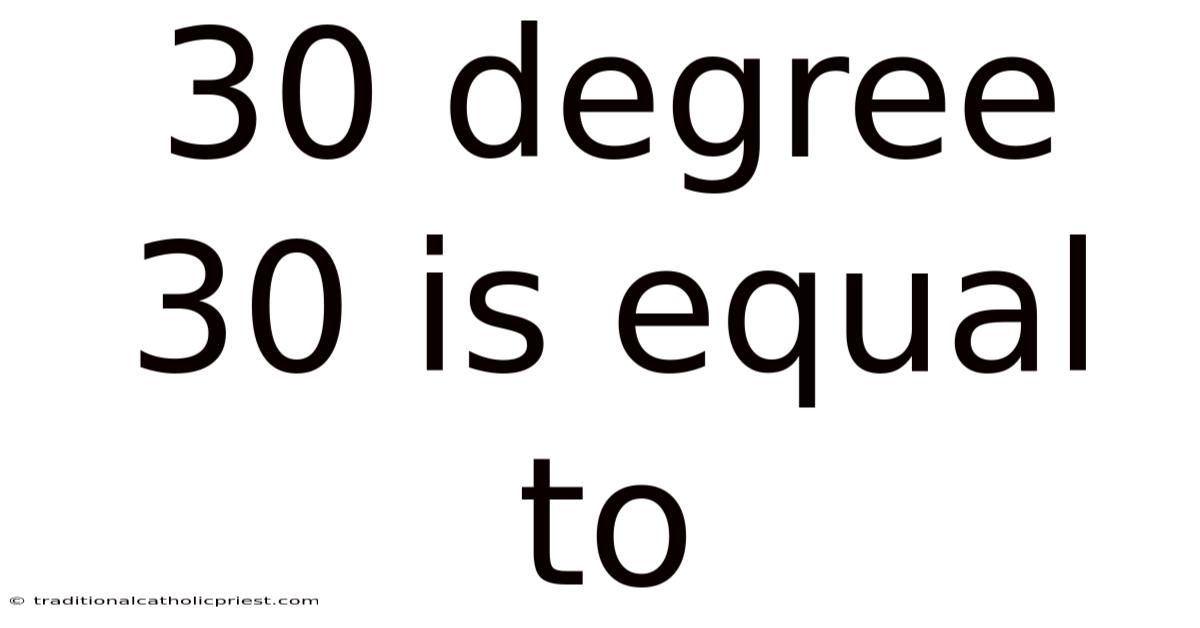
Table of Contents
Have you ever paused to consider the seemingly simple statements we often take for granted in mathematics? It's easy to breeze through equations and formulas, accepting them at face value. But what happens when we truly dissect and explore these fundamental concepts? Sometimes, the deeper we delve, the more fascinating and unexpected the results become. Let's embark on an exploration of one such statement: "30 degrees equals π/6 radians."
At first glance, "30 degrees = π/6" might seem like a straightforward conversion, easily dismissed as another mathematical fact. However, by unpacking this seemingly simple statement, we uncover the interconnectedness of geometry, trigonometry, and the very nature of angular measurement. In this article, we will unravel the significance of this equation, journeying through the underlying principles that make it true and the profound implications it holds in various fields of mathematics and beyond.
Main Subheading: Unpacking the Concept of Angular Measurement
Angles are a cornerstone of geometry and trigonometry, defining the relationships between lines, shapes, and spatial orientations. To truly understand why 30 degrees equals π/6 radians, we first need to appreciate the nuances of how angles are measured. The two primary units for measuring angles are degrees and radians, each offering a distinct perspective. Degrees, perhaps the more familiar unit, divide a full circle into 360 equal parts. Radians, on the other hand, relate an angle to the arc length it subtends on a circle.
The choice between degrees and radians often depends on the context. In everyday applications, such as navigation or construction, degrees might seem more intuitive. However, in advanced mathematics and physics, radians often simplify calculations and reveal deeper mathematical relationships. The conversion between these two units isn't arbitrary; it's rooted in the fundamental properties of circles and the relationships between their circumferences and radii. Understanding this relationship is key to grasping the significance of the equation "30 degrees = π/6".
Comprehensive Overview: Degrees, Radians, and Their Relationship
Let’s delve deeper into the definitions, scientific foundations, and history of degrees and radians to truly understand their relationship.
Degrees: A Historical Perspective
The degree as a unit of angular measurement traces its origins back to ancient civilizations, particularly the Babylonians. Their choice of 360 degrees for a full circle wasn't arbitrary; it was likely influenced by their number system (base 60) and their astronomical observations. Dividing the year (approximately 365 days) into 360 segments provided a convenient way to track celestial movements. This historical convention has persisted for millennia, making degrees a widely recognized and used unit for measuring angles in various practical applications.
One full rotation, or a complete circle, is defined as 360 degrees (360°). A straight line forms an angle of 180° (half a circle), and a right angle measures 90° (a quarter of a circle). Degrees are further subdivided into minutes and seconds, where one degree equals 60 minutes (60') and one minute equals 60 seconds (60"). While degrees are intuitive for many, they can sometimes complicate mathematical formulas, especially in calculus and other advanced areas.
Radians: A Natural Measure
Radians offer a different perspective on angular measurement, one that connects angles directly to the properties of a circle. One radian is defined as the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius of the circle. This definition makes radians a "natural" unit for angular measurement, particularly in mathematical contexts.
The circumference of a circle is given by the formula C = 2πr, where r is the radius. This means that a full circle has an arc length of 2π times the radius. Therefore, a full circle corresponds to an angle of 2π radians. This direct relationship between the angle in radians and the arc length simplifies many mathematical formulas, especially in calculus, physics, and engineering.
The Conversion Factor: Bridging Degrees and Radians
The key to understanding the equation "30 degrees = π/6" lies in the conversion factor between degrees and radians. Since a full circle is 360 degrees and also 2π radians, we can establish the following relationship:
360° = 2π radians
Dividing both sides by 360, we get:
1° = (2π/360) radians = (π/180) radians
This gives us the conversion factor: to convert from degrees to radians, multiply by π/180. Conversely, to convert from radians to degrees, multiply by 180/π.
Applying the Conversion: 30 Degrees to Radians
Now, let's apply this conversion factor to the specific case of 30 degrees:
30° = 30 * (π/180) radians
Simplifying the fraction, we get:
30° = (30/180) * π radians = (1/6) * π radians = π/6 radians
Therefore, 30 degrees is indeed equal to π/6 radians. This conversion highlights the consistent relationship between the two units of angular measurement and reinforces the fundamental connection between geometry and trigonometry.
Why Radians Matter: Applications in Mathematics and Physics
Radians are not just an abstract mathematical concept; they are crucial in many areas of science and engineering. In calculus, for instance, the derivatives of trigonometric functions are much simpler when angles are expressed in radians. For example, the derivative of sin(x) with respect to x is cos(x) only when x is in radians. If x were in degrees, the derivative would involve an additional constant factor.
In physics, radians are essential in describing rotational motion. Angular velocity (ω) is typically measured in radians per second, and angular acceleration (α) in radians per second squared. Using radians simplifies the equations relating linear and angular quantities. For instance, the linear velocity v of a point on a rotating object is given by v = rω, where r is the distance from the point to the axis of rotation, and ω is the angular velocity in radians per second.
Trends and Latest Developments
In recent years, the use of radians has become even more prevalent with advancements in computing and simulation technologies. Many software packages and programming languages designed for scientific and engineering applications default to using radians for trigonometric functions and angular calculations. This shift reflects the increasing recognition of radians as the more natural and mathematically convenient unit for angular measurement in these contexts.
Furthermore, educational curricula worldwide are placing greater emphasis on the importance of radians. Students are being introduced to radians earlier in their mathematical education to foster a deeper understanding of trigonometry and its applications. This trend aims to equip future scientists and engineers with the tools they need to tackle complex problems involving angular measurements with confidence and proficiency.
Professional insights reveal that a strong grasp of radians is particularly important in fields such as robotics, computer graphics, and signal processing. In robotics, radians are used extensively in controlling the movements of robotic arms and other articulated systems. In computer graphics, radians are essential for performing rotations and other transformations of objects in three-dimensional space. In signal processing, radians are used to represent the frequencies of signals, which are then used in various filtering and analysis techniques.
Tips and Expert Advice
Mastering the conversion between degrees and radians and understanding their applications can significantly enhance your problem-solving skills in mathematics, physics, and engineering. Here are some practical tips and expert advice to help you along the way:
-
Memorize Key Conversions: It's helpful to memorize the radian equivalents of common angles like 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360°. Knowing these conversions by heart will save you time and effort in many calculations. For example, knowing that 45° is equal to π/4 radians can quickly simplify trigonometric expressions.
-
Practice, Practice, Practice: The more you practice converting between degrees and radians, the more comfortable you'll become with the process. Work through various examples, and try to visualize the angles on a unit circle to reinforce your understanding. For instance, try converting angles like 15°, 75°, 120°, and 330° to radians, and vice versa.
-
Understand the Unit Circle: The unit circle is a powerful tool for visualizing trigonometric functions and understanding the relationship between degrees and radians. By plotting angles on the unit circle, you can easily determine their sine, cosine, and tangent values. Also, the unit circle provides a visual representation of how radians relate to arc length.
-
Use a Calculator: When dealing with more complex angles or when accuracy is paramount, don't hesitate to use a calculator to perform the conversion. Most scientific calculators have built-in functions for converting between degrees and radians. Make sure you understand how to use these functions correctly to avoid errors.
-
Pay Attention to Units: Always pay close attention to the units you're working with. When solving problems involving angles, make sure you're using the correct units (degrees or radians) and that you're converting between them when necessary. Mixing up the units can lead to incorrect results.
-
Apply Radians in Real-World Problems: To solidify your understanding of radians, try applying them to real-world problems. For example, you could use radians to calculate the distance traveled by a point on a rotating wheel, or to determine the angle of elevation of a satellite in orbit.
By following these tips and practicing regularly, you can develop a strong understanding of degrees and radians and their applications. This will not only improve your performance in mathematics and science courses but also prepare you for more advanced studies and careers in fields where angular measurement is critical.
FAQ
Q: Why are there 360 degrees in a circle?
A: The choice of 360 degrees for a full circle is historical, likely originating from the Babylonians who used a base-60 number system. It was also convenient for tracking astronomical movements, as it approximated the number of days in a year.
Q: Is there any advantage to using degrees over radians?
A: Degrees are often more intuitive for everyday applications, such as navigation or construction, where precise mathematical calculations are not always necessary. However, radians are generally preferred in advanced mathematics and physics due to their simplicity and direct relationship to arc length.
Q: How do I convert from radians to degrees?
A: To convert from radians to degrees, multiply the radian measure by 180/π. For example, to convert π/3 radians to degrees, you would calculate (π/3) * (180/π) = 60 degrees.
Q: What is a radian in simple terms?
A: A radian is the angle created when the length of the arc of a circle is equal to the radius of the circle.
Q: Are radians used in real-world applications?
A: Yes, radians are widely used in various fields, including physics, engineering, computer graphics, robotics, and signal processing. They simplify calculations and provide a more natural way to express angular relationships.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the equation "30 degrees = π/6" is far more than a simple conversion. It embodies the fundamental relationship between degrees and radians, two essential units for measuring angles. Understanding this relationship is crucial for success in mathematics, physics, and various engineering disciplines. By mastering the conversion between degrees and radians and appreciating the underlying principles, you can unlock a deeper understanding of the world around you and tackle complex problems with confidence.
Now that you've explored the significance of "30 degrees = π/6 radians," take the next step! Practice converting between degrees and radians, explore the unit circle, and apply your knowledge to real-world problems. Share your insights and questions in the comments below, and let's continue this journey of mathematical discovery together!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 30 Degree 30 Is Equal To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.