28 5 2 3 X 3
catholicpriest
Nov 25, 2025 · 13 min read
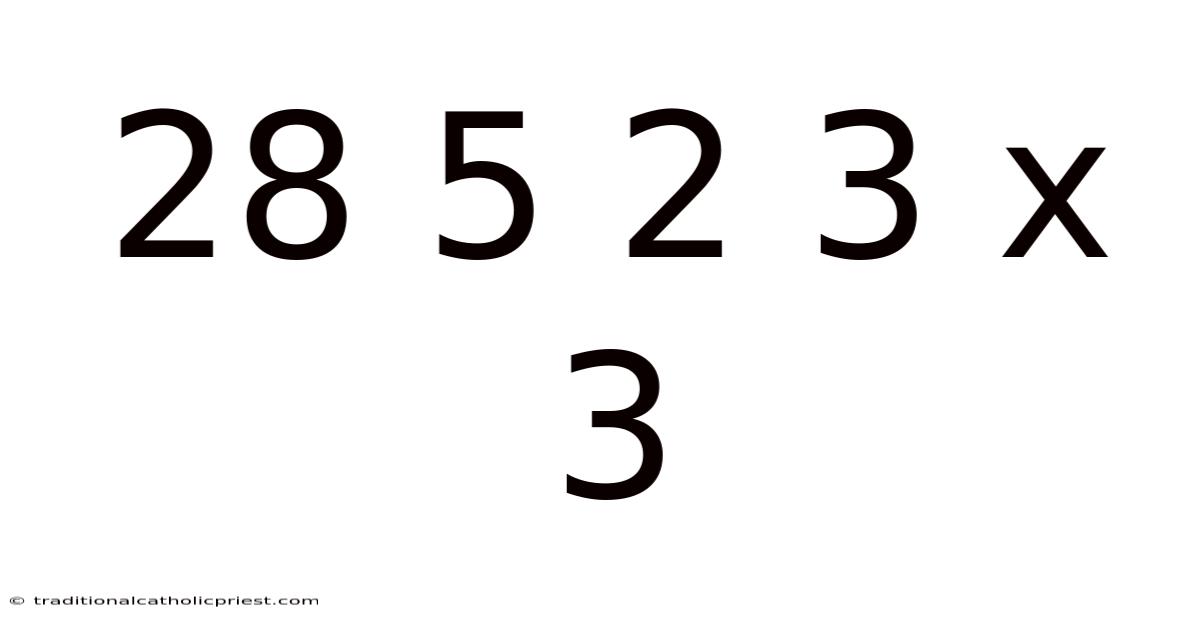
Table of Contents
The cryptic sequence "28 5 2 3 x 3" might initially appear as a random assortment of numbers and symbols. However, within the realm of mathematics and problem-solving, such sequences often hold deeper meaning, representing a coded puzzle, a mathematical operation, or even a set of instructions within a broader algorithm. Unraveling the significance of "28 5 2 3 x 3" requires a systematic approach, breaking down the components and exploring potential interpretations within different mathematical contexts.
At first glance, we see a combination of single and double-digit numbers, followed by a multiplication symbol and another single-digit number. This immediately suggests the possibility of an arithmetic problem. However, without further context, several interpretations are possible. We could treat the sequence as separate numbers to be manipulated, or consider it a set of indices pointing to elements within a larger dataset. The "x 3" element strongly hints at a scaling operation or a multiplication factor affecting other numbers in the sequence. This article explores various possibilities surrounding the mathematical expression "28 5 2 3 x 3," offering a comprehensive overview of its potential meanings and applications.
Unpacking the Numerical Sequence
The sequence "28 5 2 3 x 3" is intriguing because it is not immediately obvious what operation or context it refers to. Before diving into potential interpretations, let's first consider some foundational mathematical concepts that will help us understand the possibilities.
Numbers and Operations: The sequence consists of integers, which are fundamental building blocks in mathematics. Integers can be positive, negative, or zero. In this case, we have positive integers. The "x" symbol typically denotes multiplication, one of the basic arithmetic operations, alongside addition (+), subtraction (-), and division (/).
Order of Operations: When evaluating mathematical expressions, the order of operations is crucial. The acronym PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) or BODMAS (Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction) dictates the sequence in which operations should be performed to obtain the correct result. If the sequence "28 5 2 3 x 3" is meant to be an arithmetic expression, understanding the order of operations will be vital.
Mathematical Context: The interpretation of the sequence depends heavily on the context. Is it part of a coding problem, a statistical analysis, or a geometric calculation? Each context brings its own set of rules and conventions. For example, in computer science, the sequence might represent array indices, whereas in statistics, it could relate to data points within a dataset.
Potential Interpretations: Given these foundations, we can consider a few potential interpretations:
- Simple Arithmetic: Treating the sequence as an arithmetic expression might involve performing multiplication first, according to the order of operations. However, the presence of multiple numbers without explicit operators between them raises questions.
- Matrix or Vector Operations: The sequence could represent dimensions or elements of matrices or vectors, where "x" denotes a cross product or scalar multiplication.
- Indexing or Referencing: In computer science or data analysis, the numbers might serve as indices to retrieve specific elements from arrays, lists, or data frames.
- Coded Message: The sequence could be part of a coded message, where each number corresponds to a letter, word, or symbol based on a predefined cipher or algorithm.
To further unpack the meaning, we need to explore each of these interpretations in detail.
Comprehensive Overview of Possible Interpretations
The beauty of a sequence like "28 5 2 3 x 3" lies in its ambiguity. It invites exploration and the application of various mathematical principles. Let's delve into different scenarios and how the sequence might be interpreted within each.
1. Direct Arithmetic Interpretation
The most straightforward approach is to consider the sequence as a potential arithmetic expression. However, the lack of operators between the initial numbers complicates this interpretation. If we strictly adhere to the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS), the multiplication "3 x 3" would be performed first, resulting in 9. The sequence then becomes "28 5 2 9".
Without additional operators, there's no mathematically valid way to combine these numbers into a single expression. One could hypothesize implicit addition or subtraction between the numbers, but this lacks a solid basis without further information.
For instance, if the implied operation was addition, the expression would be:
28 + 5 + 2 + (3 x 3) = 28 + 5 + 2 + 9 = 44
Alternatively, if the context suggested a series of operations to be applied sequentially, it might look like:
- Start with 28
- Add 5: 28 + 5 = 33
- Add 2: 33 + 2 = 35
- Multiply 3 by 3: 3 x 3 = 9
- Add 9: 35 + 9 = 44
While arithmetically possible, these interpretations are speculative without additional context or a clear set of rules.
2. Matrix or Vector Representation
In linear algebra, matrices and vectors are fundamental concepts. The "x" symbol often represents the cross product of two vectors or scalar multiplication of a matrix. If we interpret "28 5 2 3" as components of vectors or elements of matrices, several possibilities arise.
Vectors: We could interpret "5 2 3" as a vector, and "x 3" as scalar multiplication. However, the number "28" is left without a clear role in this interpretation. One possible construction would be:
Let v = [5, 2, 3]
Then, 3v = [15, 6, 9]
If "28" represents some external parameter, like an offset or a constant to be added to each component, the interpretation might make more sense within a specific problem domain.
Matrices: The numbers might represent elements of a matrix, but the dimensions are not immediately clear. If we assume a 2x2 matrix formed from "5 2 3 x", with "x" representing an unknown, the "28" is still unaccounted for. However, if the "x" symbolizes multiplication, and we are considering a transformation or scaling, it could be interpreted in a more complex manner.
For instance, consider a scenario where "28" represents the determinant of a transformation matrix applied to a vector constructed from "5 2 3", scaled by a factor of 3. This interpretation is significantly more involved and requires substantial background knowledge of linear algebra.
3. Indexing and Referencing
In computer science and data analysis, sequences of numbers are frequently used as indices to access elements within data structures like arrays, lists, or data frames. The sequence "28 5 2 3" could potentially represent indices, and "x 3" could suggest repeating the retrieval process three times or applying a function three times to the retrieved element.
For example, in Python:
data = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100] # Sample data
indices = [5, 2, 3]
results = [data[i] for i in indices] # Accessing elements at specified indices
print(results) # Output: [60, 30, 40]
Here, "5," "2," and "3" are indices that retrieve elements from the data list. The "28" is left unused unless the data list is extended or the indices are modified. The "x 3" could then indicate some operation repeated on the results list.
Alternatively, in data analysis with libraries like Pandas:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'col1': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
'col2': [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60]})
indices = [2, 3]
selected_rows = df.iloc[indices] # Selecting rows based on indices
print(selected_rows)
In this context, "2" and "3" are indices for selecting rows from a Pandas DataFrame. Again, "28" remains without a direct interpretation in this scenario, and "x 3" might refer to some iterative processing on the selected rows or columns.
4. Coded Message
The sequence "28 5 2 3 x 3" could potentially be part of a coded message. In cryptography, numerical sequences are often used to represent letters, words, or symbols based on a predefined cipher or algorithm.
Simple Substitution Cipher: Each number could represent a letter in the alphabet (A=1, B=2, ..., Z=26). In this case:
- 28: Would need to extend the alphabet or use a modular arithmetic approach (28 mod 26 = 2, which is 'B')
- 5: E
- 2: B
- 3: C
The "x 3" might signify repeating the decoding process or applying some transformation to the decoded letters. The decoded sequence "BEBC" followed by some further transformation is a possibility.
Polyalphabetic Cipher: The numbers could represent positions in a polyalphabetic substitution table. More complex ciphers might use keys or algorithms to shift the numerical values or manipulate them in various ways. The "x 3" could denote a key length or a repetition factor in the encryption/decryption process.
Word or Phrase Mapping: Each number could correspond to a specific word or phrase defined in a lookup table or codebook. The "x 3" might indicate repeating a phrase three times or combining the phrases in a specific order.
Decoding this type of message requires knowledge of the specific cipher or coding scheme used. Without this, interpreting the sequence as a coded message remains highly speculative.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the specific sequence "28 5 2 3 x 3" may not be directly discussed in academic literature or industry trends, the principles and concepts used to interpret it are constantly evolving.
Mathematics Education: There is a growing emphasis on problem-solving and critical thinking in mathematics education. Sequences and puzzles like this one are valuable tools for developing these skills. Educators are increasingly using open-ended problems that have multiple possible solutions, encouraging students to explore different approaches and justify their reasoning.
Data Science and Analytics: In data science, pattern recognition and sequence analysis are crucial. Algorithms for sequence mining, time series analysis, and anomaly detection are continuously being refined. Techniques like recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and transformers are used to analyze and predict sequences of data, whether it's stock prices, weather patterns, or user behavior.
Cryptography and Security: Cryptography remains a critical field in computer science. New encryption algorithms are constantly being developed to protect data from unauthorized access. Modern cryptography often involves complex mathematical operations on numerical sequences, using techniques like elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) and homomorphic encryption.
Algorithmic Problem Solving: Platforms like LeetCode, HackerRank, and Kaggle host coding challenges and competitions that often involve analyzing and manipulating numerical sequences. These challenges test participants' ability to apply algorithms, data structures, and mathematical principles to solve complex problems efficiently.
Artificial Intelligence: AI systems, particularly those involving natural language processing (NLP), use numerical representations of text and data. Techniques like word embeddings (e.g., Word2Vec, GloVe) map words to numerical vectors, allowing AI models to understand semantic relationships between words. Numerical sequences are fundamental to how AI models process and generate text.
Tips and Expert Advice
Interpreting mathematical sequences like "28 5 2 3 x 3" requires a combination of logical reasoning, mathematical knowledge, and contextual awareness. Here are some practical tips and expert advice for approaching such problems:
1. Start with the Basics:
Begin by considering the most straightforward interpretations. Can the sequence be treated as a simple arithmetic expression? Are there any obvious mathematical operations that can be applied? Avoid jumping to complex solutions without first exhausting the basic possibilities.
Example: Before considering matrix operations or complex ciphers, try treating the numbers as individual values and see if basic arithmetic (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) yields a meaningful result within a specific context.
2. Consider the Context:
The context in which the sequence appears is crucial. Is it part of a coding challenge, a data analysis task, or a mathematical puzzle? The context will provide valuable clues about the intended interpretation.
Example: If the sequence appears in a programming context, consider whether the numbers might represent array indices, loop counters, or input parameters to a function. If it appears in a financial analysis report, consider whether the numbers might represent stock prices, trading volumes, or financial ratios.
3. Break Down the Problem:
Decompose the sequence into smaller parts and analyze each part separately. Identify patterns, relationships, and potential operations. The "x 3" element, for example, strongly suggests a scaling operation or repetition.
Example: Analyze the individual numbers (28, 5, 2, 3) and look for any special properties. Are they prime numbers, Fibonacci numbers, or part of a known mathematical series? The "x 3" element should be considered separately to understand how it modifies or affects the other numbers in the sequence.
4. Explore Different Mathematical Domains:
Be open to exploring different mathematical domains and concepts. The sequence might involve linear algebra, calculus, number theory, or statistics. Familiarize yourself with fundamental concepts in each domain to broaden your problem-solving toolkit.
Example: If basic arithmetic does not yield a meaningful interpretation, consider whether the sequence might relate to matrix operations, vector transformations, or statistical distributions. Brush up on the relevant concepts and formulas in these areas.
5. Look for Patterns and Relationships:
Identify any patterns or relationships between the numbers in the sequence. Are they increasing, decreasing, or alternating? Is there a constant difference or ratio between consecutive numbers? Patterns can provide valuable clues about the underlying structure of the sequence.
Example: If the numbers are increasing or decreasing, consider whether they follow an arithmetic or geometric progression. If the numbers are alternating, consider whether they represent terms in an alternating series or components of a complex number.
6. Use Computational Tools:
Utilize computational tools like calculators, spreadsheets, and programming languages to explore different interpretations. These tools can help you perform calculations, generate sequences, and visualize data.
Example: Use a spreadsheet to perform arithmetic operations on the numbers in the sequence. Use a programming language to generate sequences based on different formulas or algorithms. Use data visualization tools to plot the numbers and look for patterns.
7. Seek External Resources:
Consult external resources like textbooks, online forums, and expert communities to get help and insights. Other mathematicians, programmers, and problem-solvers may have encountered similar sequences and can offer valuable advice.
Example: Search online forums or Q&A sites for discussions about similar mathematical sequences. Consult textbooks on number theory, linear algebra, or cryptography for relevant concepts and techniques. Reach out to experts in these fields for advice and guidance.
FAQ
Q: What is the most likely interpretation of "28 5 2 3 x 3"? A: Without additional context, there is no single "most likely" interpretation. The meaning depends entirely on the problem domain and the intended application. Simple arithmetic, indexing, or coded message are all possibilities.
Q: Can "28 5 2 3 x 3" represent a valid mathematical equation? A: Not directly, without additional operators or context. As a bare sequence, it's not a complete equation. It needs further definition to become mathematically valid.
Q: Is there a specific area of mathematics that deals with sequences like this? A: Number theory, combinatorics, and discrete mathematics often deal with sequences and patterns. Depending on the interpretation, linear algebra or cryptography might also be relevant.
Q: How does the "x 3" affect the interpretation of the sequence? A: The "x 3" generally indicates some form of multiplication, scaling, or repetition. It could be a scalar multiplication factor, a repetition count, or a key length in a cipher.
Q: Can I use a computer program to find the meaning of "28 5 2 3 x 3"? A: Yes, depending on the interpretation. You can use programming languages to test different arithmetic operations, generate sequences, or decode potential coded messages. The program would need to be tailored to a specific hypothesis about the sequence's meaning.
Conclusion
The numerical sequence "28 5 2 3 x 3" presents a fascinating puzzle that highlights the importance of context and interpretation in mathematics. We've explored various possibilities, from simple arithmetic and matrix operations to indexing schemes and coded messages. The absence of a definitive answer underscores the open-ended nature of mathematical exploration and the need for clear problem definitions.
Ultimately, understanding the true meaning of "28 5 2 3 x 3" requires additional information or a specific problem setting. By systematically exploring different interpretations and applying relevant mathematical principles, we can narrow down the possibilities and potentially uncover the intended solution.
Now it's your turn! What do you think "28 5 2 3 x 3" could mean? Share your ideas and interpretations in the comments below. Let's work together to unravel this mathematical mystery!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 28 5 2 3 X 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.